What Is Fuel?
Fuel is any material that can store potential energy and release it through combustion or another chemical reaction to produce power. It is the essential energy source for engines, power plants, industrial furnaces, and heating systems. Fuels exist in various forms liquid, gaseous, and solid, and each type has different chemical properties, viscosity, and energy density, which influence how it is stored, transported, and measured.
Accurate fuel measurement is crucial because even a small error can lead to significant financial losses, process inefficiencies, or equipment malfunctions. That’s where عدادات تدفق الوقود في اللعب.
جدول المحتويات
Types of Fuel
Liquid Fuels
Common liquid fuels include diesel, gasoline, kerosene, jet fuel, biodiesel, and heavy oil.
- Diesel: High viscosity, commonly used in industrial engines and generators. Measurement challenges include temperature-dependent density changes and potential air bubbles.
- البنزين: Low viscosity and volatile, requiring precise sealing and vapor management in flow measurement.
- Kerosene and Jet Fuel: Require high accuracy and cleanliness; contamination can affect performance.
- Biodiesel: More viscous and may contain impurities that affect flow meter stability and calibration.
- Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO): Very viscous and often needs to be heated before measurement. This can complicate installation and calibration.
Gaseous Fuels
Typical gaseous fuels include natural gas, propane, butane, and hydrogen.
- الغاز الطبيعي: Compressible, and its density changes significantly with temperature and pressure.
- Propane and Butane: Stored under pressure as liquids and converted to gas for combustion, requiring accurate flow control during phase change.
- Hydrogen: Extremely low molecular weight and high diffusivity, which makes measurement sensitive and requires specialized equipment.
Each fuel type poses unique challenges in measurement. Factors like viscosity, temperature, compressibility, and impurities all influence flow meter selection. Therefore, understanding fuel characteristics is the first step in choosing the right مقياس تدفق الوقود.
What Is a Fuel Flow Meter?
A مقياس تدفق الوقود is an instrument designed to measure the rate and total quantity of fuel flowing through a pipe or system. Depending on the measurement principle, it can measure التدفق الكتلي (the actual amount of fuel) or التدفق الحجمي (the volume the fuel occupies).
Fuel flow meters are widely used in:
- Automotive and marine engine testing
- Power generation systems
- Industrial furnaces and burners
- Fuel distribution and transfer systems
- Aerospace and laboratory testing setups
The primary goal of a fuel flow meter is to provide accurate, repeatable measurements regardless of changes in temperature, pressure, or fuel type.
Best Recommended Fuel Flow Meters
أجهزة قياس التدفق بالإزاحة الإيجابية (PD)
مبدأ العمل: PD meters directly measure the fuel volume by trapping fixed quantities between internal moving parts.
المزايا:
- دقة عالية جدًا (± 0.1-0.5%)
- Ideal for measuring viscous liquids such as diesel, lubricants, and heavy oils
- Unaffected by changes in flow profile or viscosity القيود:
- Not suitable for dirty fluids with large particles
- Requires regular maintenance due to mechanical wear
الأفضل لـ Diesel, heavy oil, and lubricating oil applications.
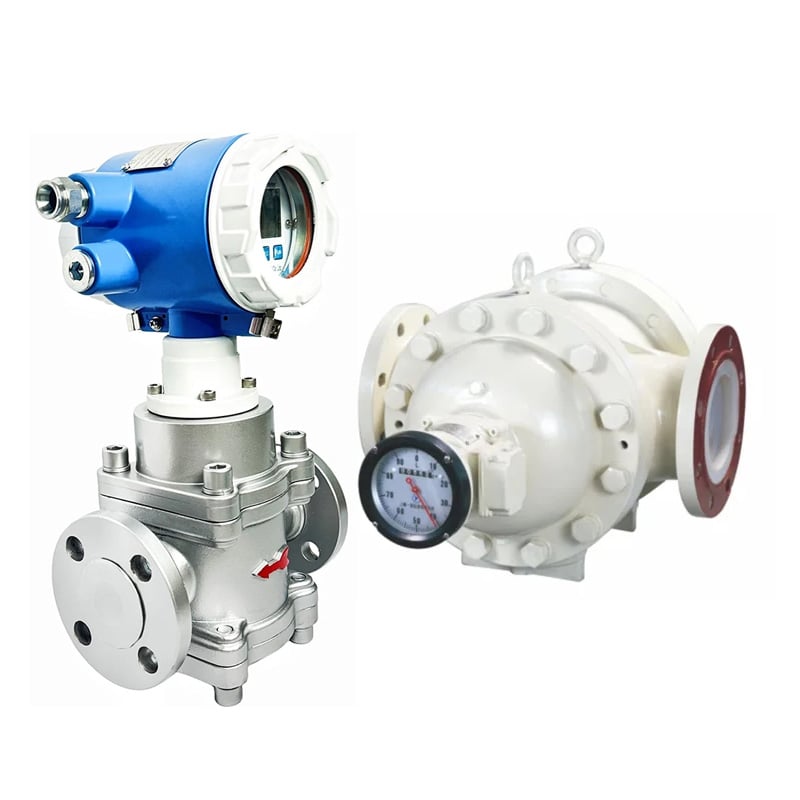

مقياس التدفق بالإزاحة الإيجابية ثنائي الدوار (MT-ABR)
- دقة عالية تصل إلى ± 0.1 ± 0.%، وضغط معالجة عالٍ يصل إلى 110 بار (1595 رطل لكل بوصة مربعة)
- عمر افتراضي طويل للغاية، وصيانة اقتصادية منخفضة الصيانة
- مستقر في الجري بصوت منخفض
- أداء جيد ضد التداخل وعمر خدمة طويل
- قابلية تطبيق قوية لتغيرات اللزوجة

مقياس التدفق المنخفض الإزاحة الموجبة للتدفق بالتروس ذات الإزاحة الإيجابية MT-GF
- مصممة للسوائل منخفضة التدفق من 0.6 لتر/ساعة
- مصممة لقياس السوائل عالية اللزوجة، والتعامل مع الوسائط الصعبة مثل الشراب والأسفلت المنصهر والعسل بدقة موثوقة
- قياس عالي الدقة بدقة تصل إلى ± 0.51 تيرابايت 3 تيرابايت
- 150:1 wide turndown ratio
مقاييس تدفق كوريوليس
مبدأ العمل: Measures mass flow directly by detecting the Coriolis force generated as fuel flows through vibrating tubes.
المزايا:
- Measures true mass flow independent of temperature or pressure
- High accuracy (±0.1–0.2%)
- Can measure density and temperature simultaneously القيود:
- تكلفة أولية أعلى
- Sensitive to vibration in large pipelines
الأفضل لـ Precision fuel dosing, engine testing, and high-value applications involving various liquid or gaseous fuels.
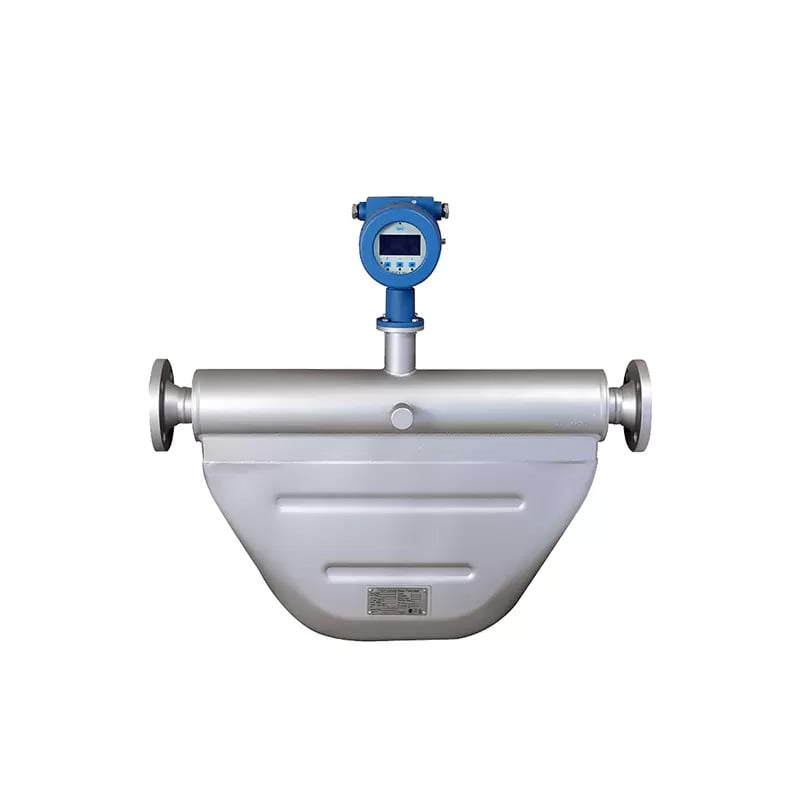

مقياس التدفق الكتلي كوريوليس W الشكل (MTD-ACMW)
- دقة عالية تصل إلى ± 0.1 %، موثوقية جيدة
- أداء جيد في انعدام الاستقرار ومقاومة التداخلات
- لا توجد أجزاء متحركة، لا تحتاج إلى صيانة

مقياس التدفق الكتلي كوريوليس/جهاز التحكم في التدفق الكتلي MTL20FE
- مصممة لقياس الغاز/السائل منخفض التدفق.
- دقة عالية وتكرار جيد. بالنسبة للسوائل، يمكن أن تصل دقة القياس إلى ± 0.25%؛ وبالنسبة للغازات، يمكن أن تصل دقة القياس إلى ± 0.5%.
- نسبة الخفض: 50:1 لوحدة التحكم في التدفق الكتلي الرقمي؛ 100:1 لمقياس التدفق الكتلي الرقمي.
- زمن الاستجابة: وحدة التحكم في التدفق الكتلي <0.2 ثانية؛ مقياس التدفق الكتلي <0.1 ثانية
- وحدة تحكم PID مدمجة لتنظيم معدل التدفق.
مقاييس التدفق الحراري الكتلي
مبدأ العمل: Measures gas mass flow based on the heat dissipation rate as fuel gas passes over a heated sensor.
المزايا:
- Ideal for measuring low-flow or clean gas fuels
- Provides direct mass flow measurement without pressure or temperature compensation القيود:
- Not suitable for liquids
- Performance can be affected by humidity or particles in the gas
الأفضل لـ Natural gas, propane, and hydrogen flow measurement.

مقياس التدفق الكتلي الحراري المقاوم للانفجار (MT212-Ex)
- فئة مقاومة للانفجار: Ex db IIC IIC T6 Gb / Ex tb IIIC T80°CDb.
- مناسبة للأنابيب ذات الأقطار من DN20 إلى DN1000.
- نسبة دوران واسعة للغاية 1:2500، يتراوح نطاق القياس من 0.1 نيوتن متر/ثانية إلى 250 نيوتن متر/ثانية.
- معالجة إشارات رقمية كاملة، ودقة أعلى، وثبات طويل الأمد.
- يمكن للهيكل الكهربائي المعزول بالكامل تصفية الاضطرابات الميدانية بالكامل.

مقياس التدفق الكتلي الحراري للغاز/جهاز التحكم في التدفق الحراري للغاز (MTL20FD)
- مصممة لقياس الغاز منخفض التدفق.
- نسبة الخفض: 50:1 لوحدة التحكم في التدفق الكتلي الرقمي؛ 100:1 لمقياس التدفق الكتلي الرقمي.
- زمن الاستجابة: وحدة التحكم في التدفق الكتلي <0.2 ثانية؛ مقياس التدفق الكتلي <0.1 ثانية
- وحدة تحكم PID مدمجة لتنظيم معدل التدفق
مقاييس تدفق التوربينات
مبدأ العمل: Uses the rotation speed of a turbine blade to determine the volumetric flow rate.
المزايا:
- Good accuracy at medium to high flow rates
- Compact and cost-effective القيود:
- Sensitive to viscosity changes
- Requires stable, clean fuel
الأفضل لـ Gasoline, kerosene, or aviation fuel under clean conditions.
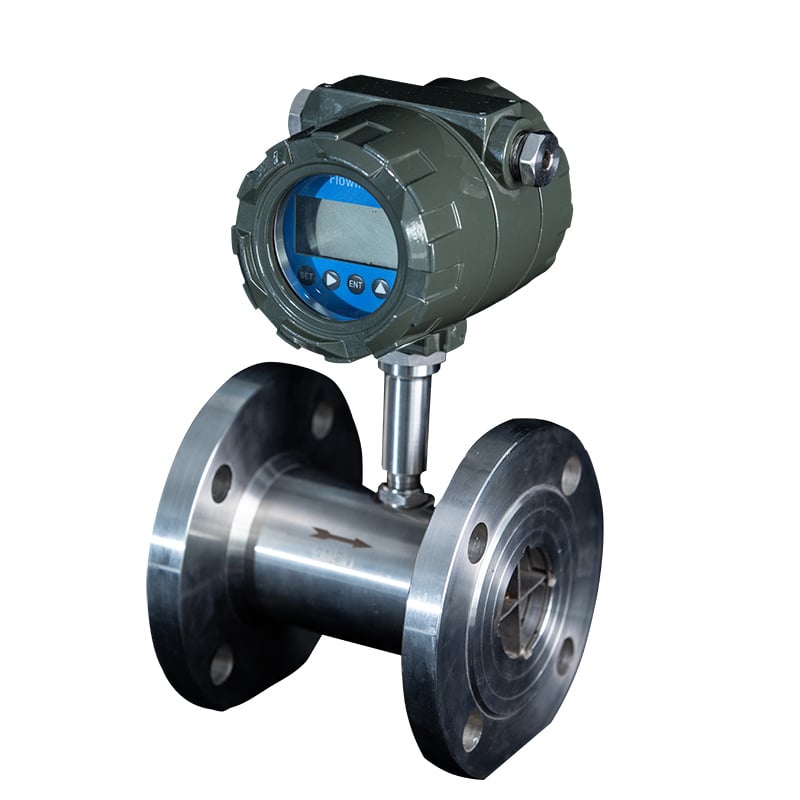

مقياس التدفق التوربيني السائل عالي الدقة (LWGYMT-AJWL)
- دقة عالية تصل إلى ± 0.2 %، مع إمكانية تكرار جيدة.
- نسبة الدوران إلى الأسفل 1:20.
- هيكل موفِّر للمساحة مع حد أدنى لحجم التجويف DN0.5.
- يمكن تخصيص الألوان والمظهر حسب الطلب
أجهزة قياس التدفق بالموجات فوق الصوتية
مبدأ العمل: Measures flow velocity using the time difference between transmitted and received ultrasonic pulses.
المزايا:
- No moving parts, minimal maintenance
- Suitable for both liquid and gas fuels
- Can be installed non-intrusively (clamp-on type) القيود:
- Accuracy depends on installation and pipe conditions
- Not ideal for very viscous or aerated fuels
الأفضل لـ Clean liquid fuels, pipeline monitoring, and large-diameter flow measurement.
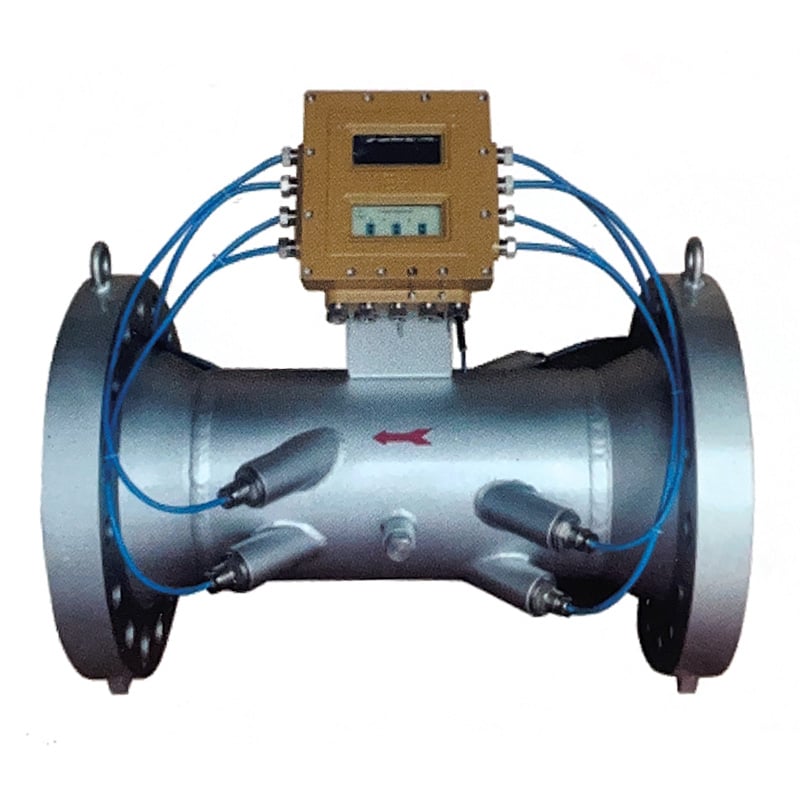

مقياس تدفق الغاز عالي الدقة بالموجات فوق الصوتية (MTS-LYNSB)
- دقة عالية للغاز تصل إلى ± 0.5%
- لا توجد أجزاء متحركة، ولا فقدان للضغط، ولا عوائق للخطوط
- لا يوجد تزييت أو صيانة دورية
- لا يتأثر القياس بخصائص الغاز
- نسبة دوران عريض 100:1
- إمكانية ثنائية الاتجاه
How to Choose the Right Fuel Flow Meter
Selecting the proper fuel flow meter depends on the type of fuel, flow conditions, accuracy requirements, and installation environment. Below are key factors to consider:
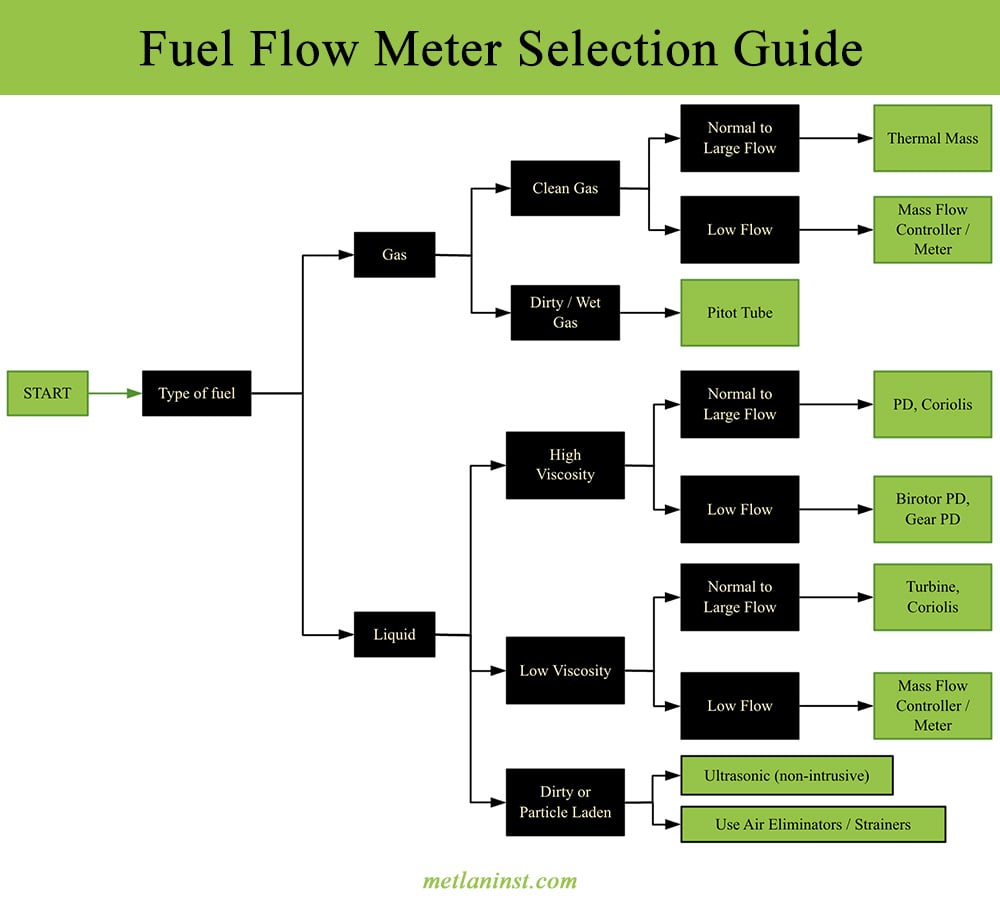
Fuel Type and Properties
Identify whether you are measuring liquid or gas fuel, its viscosity, density, and temperature range.
- For viscous liquids (diesel, oil) → choose الإزاحة الإيجابية أو Coriolis meters.
- For light liquids (gasoline, kerosene) → التوربينات أو Coriolis meters work well.
- For gas fuels (natural gas, hydrogen) → الكتلة الحرارية أو الموجات فوق الصوتية meters are preferred.
Measurement Range and Accuracy
Define the required flow range and precision level.
- Laboratory and testing setups require ±0.2% or better accuracy (Coriolis, PD).
- Industrial transfer applications may allow ±1% accuracy (Thermal Mass, Turbine).
Pressure and Temperature Conditions
High-pressure or high-temperature systems require robust sensors and materials resistant to corrosion and thermal stress. Stainless steel or specialized alloys are typically used.
Maintenance and Installation
For remote or continuous operations, select meters with صيانة منخفضة و digital output compatibility (e.g., 4–20 mA, RS485, or Modbus).
Clamp-on ultrasonic meters can be ideal when non-intrusive installation is required.
Cost and Lifecycle
Consider total ownership cost, not just the purchase price. A higher initial investment in a Coriolis or PD meter may yield long-term savings through accuracy, reduced downtime, and energy efficiency.
Fuel Flow Meter Selection Guide
| Selection Factor | Key Considerations | Recommended Flow Meter Types | Typical Fuel Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuel Phase | Determine whether the fuel is liquid أو gas. | – Liquid: Positive Displacement, Coriolis, Turbine – Gas: Thermal Mass, Ultrasonic | Liquid fuels: Diesel, Gasoline, Jet Fuel Gas fuels: Natural Gas, Propane, Hydrogen |
| اللزوجة | High-viscosity fuels require meters that handle thick, slow-moving fluids. | – High viscosity: PD, Coriolis – Low viscosity: Turbine, Coriolis | Diesel, Heavy Oil → PD/Coriolis Gasoline, Kerosene → Turbine/Coriolis |
| Accuracy Requirement | Define precision needed for your process (e.g., testing vs. monitoring). | – High accuracy (±0.2%): Coriolis, PD – Medium (±0.5%–1%): Turbine | Engine testing → Coriolis, PD, Fuel transfer → PD/Turbine |
| Cleanliness / Particle Content | Dirty or particle-laden fuels can cause mechanical wear. | – Clean fuels: Turbine, Coriolis – Dirty fuels: Ultrasonic (non-intrusive) | Biodiesel (filtered) → PD Heavy oil with impurities → Ultrasonic |
| Budget / Lifecycle Cost | Consider total cost of ownership (accuracy, maintenance, calibration). | – Low-cost: Turbine – Mid-range: PD – Premium: Coriolis | Cost-sensitive sites → Turbine Long-term precision → Coriolis |
Applications of Fuel Flow Meters
Fuel flow meters are essential in multiple sectors:
- Automotive and Marine Engines: Real-time fuel consumption monitoring and efficiency analysis.
- Aviation: Precise jet fuel measurement for safety and performance.
- Power Generation: Monitoring fuel supply to turbines and boilers.
- Oil & Gas Industry: Custody transfer, blending, and leak detection.
- Laboratory and Research: Calibration, performance testing, and emission studies.
Accurate measurement not only improves operational efficiency but also helps meet environmental and safety regulations.
A مقياس تدفق الوقود is more than just a measuring device—it is a critical component that ensures energy efficiency, process control, and cost management. Whether dealing with diesel, gasoline, natural gas, or hydrogen, selecting the right flow meter type can significantly impact performance and reliability.







