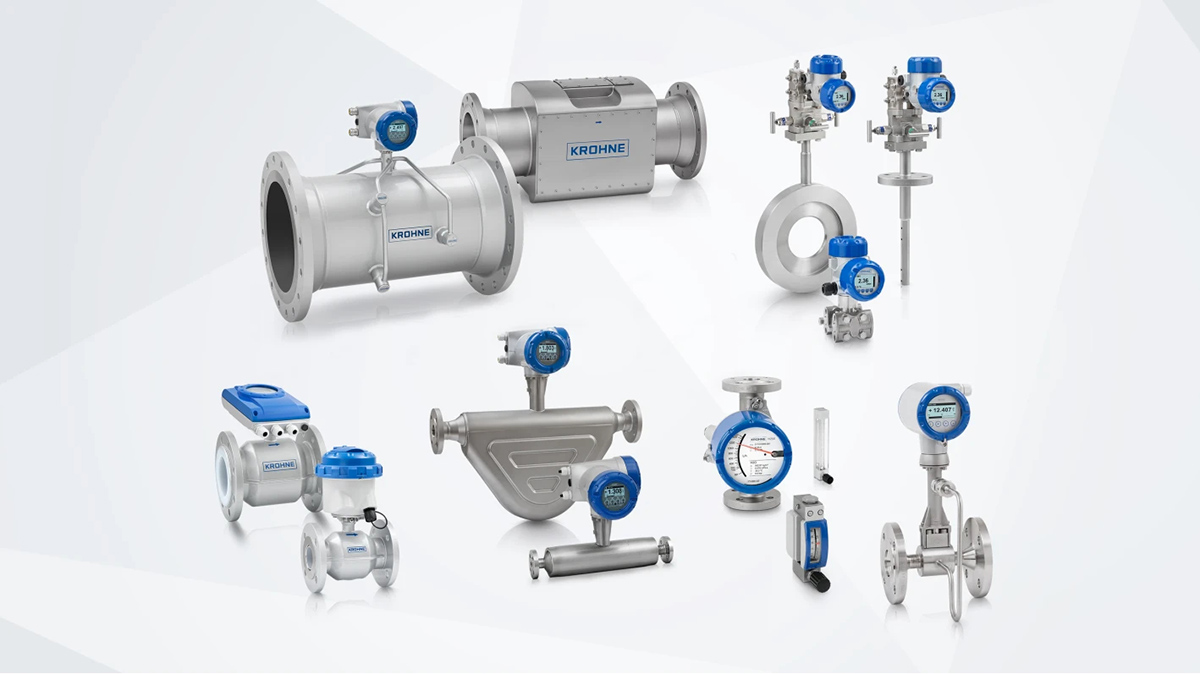
Os medidores de caudal são ferramentas essenciais utilizadas para medir o movimento de fluidos - sejam eles líquidos, gases ou vapor - em várias aplicações industriais e comerciais. A medição exacta do caudal é crucial para garantir a eficiência do processo, a conformidade regulamentar, o controlo de custos e a segurança. Os medidores de caudal são geralmente classificados em caudalímetros de pressão diferencial, caudalímetros de deslocamento positivo, medidores de caudal volumétricoe medidores de caudal mássico. Cada tipo tem caraterísticas, princípios, aplicações, vantagens e desvantagens distintas.
Índice
Relate Posts:
O que são medidores de caudal?
Os medidores de caudal são instrumentos concebidos para medir o caudal de um fluido - quer por volume (por exemplo, litros por segundo) ou massa (por exemplo, quilogramas por segundo). Os dados que fornecem são fundamentais para:
- Controlo de processos: Otimização da eficiência em sectores como o petróleo e o gás, o tratamento de águas e a indústria transformadora.
- Eficiência energética: Monitorização de caudais em sistemas AVAC.
- Faturação e conformidade: Medir com exatidão a utilização de fluidos nos serviços públicos e respeitar os regulamentos.
Diferentes medidores de caudal funcionam com base em vários princípios para se adaptarem às caraterísticas únicas dos fluidos que medem.
1. Medidores de caudal de pressão diferencial
O que é o caudalímetro de pressão diferencial?
Medidor de caudal de pressão diferencial (DP) está entre os medidores de caudal mais utilizados em todo o mundo, graças à sua simplicidade, fiabilidade e versatilidade. Medem o caudal monitorizando a queda de pressão através de uma restrição na tubagem.

Princípio de funcionamento
Os medidores de caudal DP funcionam com base em Equação de Bernoullique afirma que um aumento da velocidade de um fluido corresponde a uma diminuição da pressão. Uma constrição, como uma placa de orifício, um tubo venturi ou um bocal de fluxo, é colocada na tubagem, criando uma queda de pressão. A diferença de pressão antes e depois da constrição é utilizada para calcular o caudal.
Exemplos de medidores de caudal de pressão diferencial
| Medidores de caudal de pressão diferencial | Aplicações | Vantagens | Limitações |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medidores de caudal de placa de orifício | Sistemas de vapor, gás natural e água limpa | Design simples, económico | Perda de pressão permanente, requer manutenção frequente |
| Tubos Venturi | Líquidos limpos, oleodutos e tratamento de águas residuais | Perda de pressão mínima, elevada precisão para fluidos limpos | Design mais volumoso, custo mais elevado do que as placas de orifício |
| Bicos de fluxo | Sistemas de alta velocidade e alta pressão em centrais eléctricas e indústrias químicas | Durável, capaz de suportar condições extremas | Queda de pressão permanente, menos precisa do que os tubos venturi |
| Tubos de Pitot | Medição do caudal de ar em sistemas HVAC e condutas | Design compacto, fácil de instalar | Sensível a perturbações do fluxo, menos preciso para líquidos |
2. Medidores de caudal de deslocamento positivo
O que é um caudalímetro de deslocamento positivo?
Medidores de caudal de deslocamento positivo (PD) são dispositivos mecânicos que medem o volume real de fluido que passa através do medidor, dividindo-o em incrementos fixos. Estes medidores são altamente precisos e ideais para aplicações de baixo caudal e de fluidos viscosos.

Princípio de funcionamento
Os contadores PD utilizam componentes rotativos ou oscilantes, como pistões, engrenagens ou rotores, para criar câmaras. O fluido enche estas câmaras e o movimento dos componentes é diretamente proporcional ao volume do fluido. O número de rotações ou oscilações é registado para calcular o caudal.
Exemplos de medidores de caudal de deslocamento positivo
| Medidores de caudal de deslocamento positivo | Aplicações | Vantagens | Limitações |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medidores de engrenagens ovais | Indústria farmacêutica e agroalimentar | Elevada precisão para uma gama de viscosidades | Pode ficar obstruído com detritos ou partículas |
| Medidores de pistão rotativo | Medição de combustíveis e óleos em refinarias | Elevada precisão para aplicações viscosas e de baixo caudal | As peças móveis requerem manutenção regular |
| Medidores de engrenagens | Adesivos, xaropes, lubrificantes e tintas | Lida com fluidos de alta viscosidade, medição precisa | Não adequado para fluidos sujos com partículas |
| Medidores de disco nutridor | Contadores de água residenciais e comerciais | Conceção simples, fiável para aplicações de baixo caudal | Adequação limitada para fluxos à escala industrial |
3. Medidores de caudal volumétrico
O que são medidores de caudal volumétrico?
Os medidores de caudal volumétrico medem o caudal de fluidos por volume e por unidade de tempo. São versáteis e amplamente utilizados para líquidos limpos, gases e vapor em aplicações como a distribuição de água, sistemas AVAC e processos industriais.

Como funcionam os medidores de caudal volumétrico?
Os medidores de caudal volumétrico calculam o caudal medindo a velocidade do fluido e combinando-a com a área da secção transversal do tubo. São utilizadas diferentes tecnologias, incluindo concepções mecânicas, electromagnéticas, ultra-sónicas e baseadas em vórtices, dependendo do tipo de fluido e da aplicação.
Exemplos de medidores de caudal volumétrico
| Medidores de caudal volumétrico | Aplicações | Vantagens | Limitações |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medidores de caudal electromagnéticos (Mag Metros) | Águas residuais, lamas e processamento químico | Sem partes móveis, altamente preciso para líquidos condutores | Funciona apenas com fluidos condutores |
| Medidores de caudal Vortex | Vapor, gases industriais e líquidos com impurezas moderadas | Lida com uma vasta gama de fluidos, incluindo vapor, gases e líquidos, e é adequado para condições de alta pressão e alta temperatura | Sensível a vibrações e perturbações do fluxo |
| Medidores de caudal de turbina | Água limpa, sistemas de irrigação e sistemas HVAC | Alta precisão, compacto e leve | Sensível a partículas; as peças móveis requerem manutenção |
| Medidores de caudal ultra-sónicos | Abastecimento de água municipal, grandes condutas e sistemas AVAC | Opções não intrusivas disponíveis, adequadas para tubagens de grandes dimensões | Custo inicial elevado e menor precisão para fluidos com bolhas ou partículas |
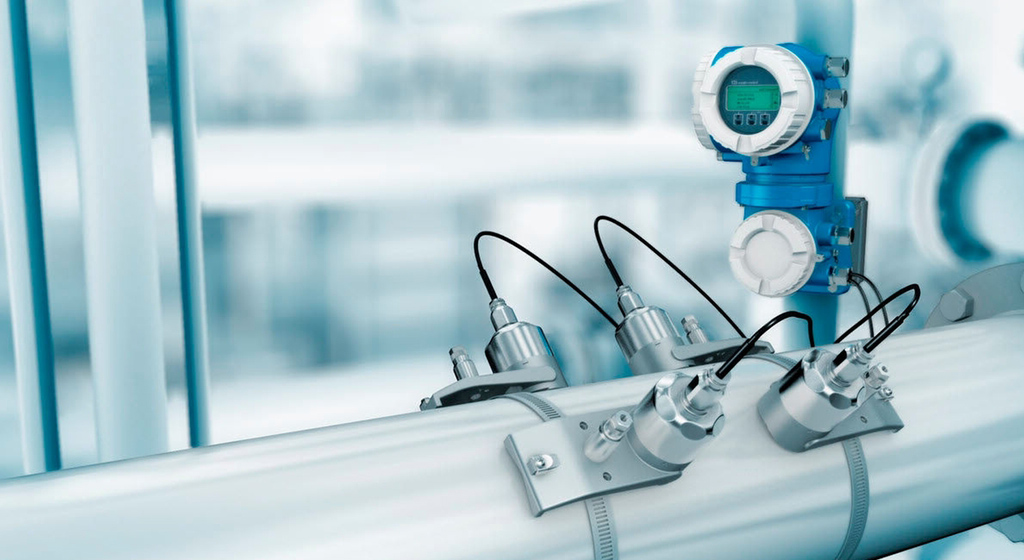
4. Medidores de caudal mássico
O que é um caudalímetro de massa?
Medidor de caudal mássico mede a massa do fluido que flui através do medidor, fornecendo dados exactos mesmo quando a densidade do fluido, a temperatura ou a pressão se alteram. São ideais para aplicações precisas como a dosagem de produtos químicos e a monitorização de gases.

Princípio de funcionamento
Os caudalímetros de massa utilizam princípios como o efeito Coriolis ou a transferência térmica de calor. Os medidores Coriolis detectam as mudanças de fase causadas pelo movimento do fluido em tubos vibratórios, enquanto os medidores térmicos medem o calor dissipado pelo fluido para calcular o caudal.
Tipos de medidores de caudal mássico
| Medidores de caudal mássico | Aplicações | Vantagens | Limitações |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medidores de caudal Coriolis | Indústrias de transformação química, alimentar e de bebidas | Medição direta da massa, extremamente precisa | Caro, sensível às vibrações |
| Medidores de caudal mássico térmico | Ar comprimido, monitorização do fluxo de gás e estudos ambientais | Ideal para gases de baixo caudal, sem peças móveis | Limitado a gases, precisão afetada pela composição do gás |
Como escolher o medidor de caudal correto
A seleção do medidor de caudal correto depende das propriedades do fluido, dos requisitos do processo e das condições de funcionamento. Aqui estão as principais considerações:
- Propriedades dos fluidos
- O fluido é um líquido, um gás ou um vapor?
- Contém partículas, é viscoso ou condutor?
- Requisitos de medição
- Necessita de dados de caudal volumétrico ou mássico?
- Que nível de precisão é necessário?
- Condições do processo
- Quais são os intervalos de temperatura e pressão?
- Existem restrições de espaço ou vibrações externas?
- Necessidades de manutenção
- É possível efetuar uma manutenção regular?
- Está à procura de soluções de baixa manutenção?
- Orçamento
- Considere tanto o custo inicial como as despesas de manutenção a longo prazo.
- Os contadores avançados, como o Coriolis, podem ter custos iniciais mais elevados, mas reduzem os custos do ciclo de vida.
Compreender os quatro principais tipos de medidores de caudal e as suas aplicações é essencial para selecionar o medidor certo. Ao avaliar as propriedades do fluido, as necessidades de precisão e o orçamento, pode garantir uma medição de caudal eficiente e fiável para a sua aplicação.








Deixar um comentário