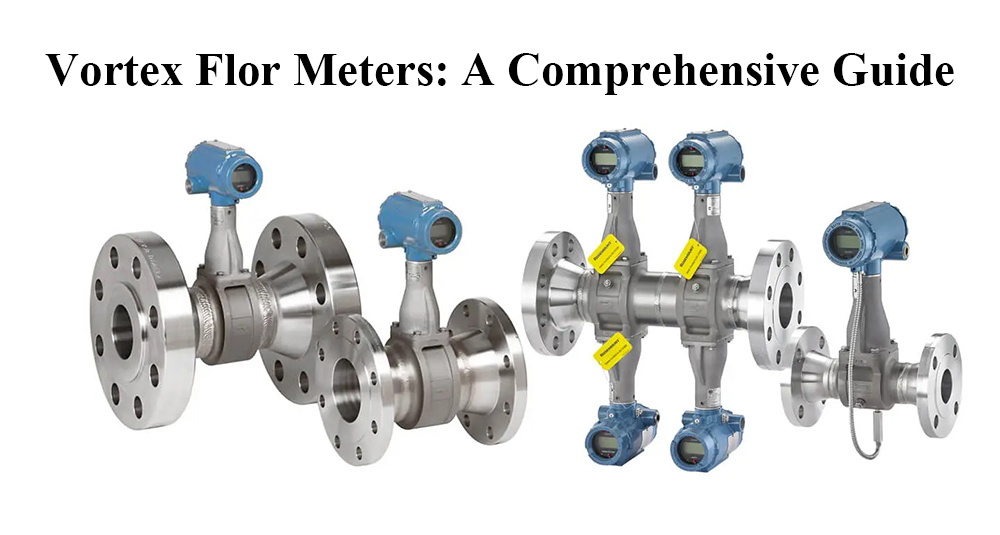
Vortex flow meters have become a popular choice for a wide range of applications when it comes to flow measurement. This guide will provide an in-depth understanding of vortex flow meters, including their working principles, types, advantages, limitations, and various applications.
Related Posts:
- What is Electromagnetic Flow Meter and How Does it Work
- Differences between vortex and turbine flow meters
Table of Contents
What is a Vortex Flow Meter?
A vortex flow meter is a type of flow measurement device that measures the volumetric flow rate of fluids, such as liquids, gases, and steam, by detecting vortices shed from a bluff body inserted into the flow stream. These meters are known for their accuracy, reliability, and ability to measure a wide range of flow rates, making them suitable for various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, water and wastewater management, and power generation.
Working Principles of Vortex Flow Meters
The operation of a vortex flow meter is based on the phenomenon known as the von Kármán effect. When a fluid flows past a bluff body—a non-streamlined object—vortices are generated alternately on either side of the body. These vortices form a repeating pattern known as a Kármán vortex street. The frequency at which these vortices are shed is directly proportional to the velocity of the fluid flow.

The fundamental relationship between vortex shedding frequency (f), fluid velocity (V), and the characteristics of the bluff body is given by the Strouhal number (St):

By measuring the frequency of vortex shedding, the flow meter calculates the velocity of the fluid. Multiplying this velocity by the cross-sectional area of the pipe provides the volumetric flow rate. Most vortex flow meters use piezoelectric, capacitive, or ultrasonic sensors to detect the pressure oscillations caused by the passing vortices.
Types of Vortex Flow Meters
Vortex flow meters can be categorized into several types based on their design, installation, and specific features. Here are the most common types:
- Inline Vortex Flow Meters:

These are the most common type of vortex flow meters, where the meter is installed directly into the pipeline. The bluff body and sensors are integrated into the flow meter body, which is sized to fit a specific pipeline diameter. They are suitable for precise flow measurements in both small and large pipes.
- Insertion Vortex Flow Meters:
Insertion vortex flow meters have a probe design, where the bluff body and sensor are inserted into the pipeline through a small opening. These meters are typically used for large pipelines where installing an inline meter would be impractical or expensive. They are cost-effective and suitable for measuring flow in large pipes with a wide range of diameters.

- Clamp-on Vortex Flow Meters:

These are non-intrusive vortex flow meters that are clamped onto the outside of the pipe. They use ultrasonic sensors to detect vortex shedding and are ideal for applications where the flow cannot be interrupted or where the pipe material cannot be penetrated. They are commonly used in temporary flow measurement setups or when retrofitting existing systems.
Advantages of Vortex Flow Meters
Vortex flow meters offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice in many industrial applications:
- Versatility:
Vortex flow meters can measure the flow of liquids, gases, and steam, making them versatile for various applications.
- High Accuracy and Repeatability:
These meters provide accurate and repeatable flow measurements with minimal drift over time, making them reliable for critical processes.
- Low Maintenance:
With no moving parts, vortex flow meters require less maintenance compared to other flow meters like turbine or positive displacement meters. This also reduces the risk of wear and tear, increasing their lifespan.
- Wide Range of Flow Rates:
Vortex flow meters are capable of measuring a wide range of flow rates, from low to high velocities, which makes them suitable for different industrial requirements.
- Unaffected by Fluid Properties:
The measurement accuracy of vortex flow meters is not significantly affected by changes in fluid properties such as viscosity, density, or temperature, making them robust for varying process conditions.
- Suitable for High-Temperature and High-Pressure Applications:
Many vortex flow meters are designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for applications involving steam and hot fluids.
Limitations of Vortex Flow Meters
Despite their numerous advantages, vortex flow meters have some limitations that should be considered when selecting them for a specific application:
- Minimum Flow Requirements:
Vortex flow meters have a minimum flow threshold below which they cannot accurately measure flow. This makes them unsuitable for very low flow rates or applications where flow can be intermittent or extremely low.
- Sensitivity to Vibration:
These meters can be sensitive to pipe vibrations, which can cause errors in flow measurement. Proper installation and support are needed to minimize the impact of vibrations.
- Pressure Drop:
The presence of a bluff body in the flow stream creates a pressure drop, which can be a concern in some applications. This pressure drop is usually small but should be accounted for in systems sensitive to pressure losses.
- Straight Pipe Requirements:
To achieve accurate measurements, vortex flow meters require a certain length of straight pipe upstream and downstream of the meter. This can limit their installation in spaces where straight pipe runs are not available.
- Not Suitable for High Viscosity Fluids:
Vortex flow meters are not ideal for measuring the flow of highly viscous fluids, as the formation of vortices is hindered by high viscosity, leading to inaccurate measurements.
Applications of Vortex Flow Meters
Vortex flow meters are used in a wide range of industries due to their versatility and reliability. Some of the common applications include:
- Oil and Gas Industry:
Vortex flow meters are extensively used in the oil and gas industry for measuring the flow of natural gas, steam, and liquids in various processes. They are particularly useful in measuring steam flow for enhanced oil recovery processes.
- Chemical and Petrochemical Industry:
In chemical plants, vortex flow meters are employed for the flow measurement of various chemicals, gases, and liquids. Their robustness and compatibility with different fluid types make them an excellent choice for such applications.
- Water and Wastewater Management:
Vortex flow meters are commonly used in water and wastewater treatment plants to measure the flow of water, slurries, and other liquids. They are especially useful for monitoring flow in large pipes and open channels.
- HVAC and Building Automation:
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, vortex flow meters are used to measure the flow of water, steam, and air for efficient energy management and system optimization.
- Power Generation:
Vortex flow meters are widely used in power plants to measure the flow of steam and cooling water, as well as natural gas, in turbines and boilers. They are particularly effective in high-temperature and high-pressure applications.
- Food and Beverage Industry:
In the food and beverage industry, vortex flow meters are used for measuring the flow of liquids such as water, juices, and other fluids. They are preferred for their sanitary designs and compatibility with clean-in-place (CIP) processes.
- Pharmaceutical Industry:
Vortex flow meters are used to measure the flow of various liquids and gases in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. Their accuracy and reliability help maintain precise control over fluid flow in critical applications.
Vortex flow meters are a valuable tool in modern industrial applications due to their versatility, accuracy, and reliability. With the ability to measure the flow of liquids, gases, and steam, they offer a range of benefits, including low maintenance, high accuracy, and suitability for harsh environments. However, it is essential to consider their limitations, such as sensitivity to vibrations and the need for minimum flow rates, when selecting a vortex flow meter for a specific application.
Overall, vortex flow meters continue to be a popular choice for flow measurement across various industries, from oil and gas to food and beverage. By understanding their working principles, types, advantages, and limitations, industries can leverage these devices to achieve efficient and accurate flow measurement, ensuring optimal process control and performance.






Leave a comment