L'un des types de débitmètres les plus importants dans ces secteurs est le débitmètre volumétrique. Comme leur nom l'indique, ces compteurs mesurent le volume d'un fluide qui les traverse, fournissant des données précises et fiables pour différentes applications industrielles. Dans cet article de blog, nous allons nous pencher sur les points suivants débitmètres volumétriquesCette brochure explique ce qu'est le débit volumétrique, les différents types de débitmètres volumétriques, leur fonctionnement et la manière de choisir celui qui convient le mieux à vos besoins.
Table des matières
Qu'est-ce que le débit volumétrique ?
Le débit volumétrique désigne le volume de fluide qui passe dans un tuyau, un conduit ou une autre canalisation au cours d'une période donnée. Il est généralement mesuré en unités telles que les litres par minute (LPM), les mètres cubes par heure (m³/h) ou les gallons par minute (GPM). La mesure du débit volumétrique est cruciale dans les industries où le maintien d'une quantité précise de fluide est nécessaire pour garantir des performances optimales et la qualité du produit.
Le débit volumétrique ne tient pas compte de la pression ou de la température du fluide ; il se concentre uniquement sur le volume de fluide qui se déplace dans une zone définie pendant une durée spécifique. Il est donc différent des autres types de mesure de débit qui peuvent se concentrer sur le débit massique, la vitesse ou les différences de pression.
Poste connexe :
Qu'est-ce qu'un débitmètre volumétrique ?
A débitmètre volumétrique est un dispositif utilisé pour mesurer le volume d'un fluide (liquide ou gaz) lorsqu'il s'écoule dans un tuyau ou une conduite. Ces compteurs mesurent directement le volume du fluide qui les traverse en capturant et en déplaçant un volume connu au cours de chaque cycle de mesure. Lorsque le fluide s'écoule dans le dispositif, le compteur enregistre le déplacement et l'utilise pour calculer le débit.
Le principal avantage des débitmètres volumétriques est leur précision. Comme ils mesurent le volume réel du fluide, ils peuvent fournir des résultats extrêmement fiables et cohérents. Ceci est essentiel pour les applications où la précision est critique, comme dans l'industrie alimentaire et des boissons, le traitement chimique et la fabrication de produits pharmaceutiques.
Les débitmètres volumétriques sont souvent préférés à d'autres types de débitmètres (comme les débitmètres de vitesse ou les débitmètres massiques) parce qu'ils fournissent une mesure directe du volume, ce qui les rend plus faciles à étalonner et à entretenir.
Types de débitmètres volumétriques et leurs principes de fonctionnement
Il existe plusieurs types de débitmètres volumétriques, chacun ayant son propre principe de fonctionnement et ses propres applications. Il s'agit notamment de débitmètres électromagnétiques, débitmètres à turbine, débitmètres à déplacement positif, débitmètres à vortexet débitmètres à ultrasons. Examinons le fonctionnement de chacun d'entre eux et les raisons pour lesquelles ils conviennent à différentes applications.
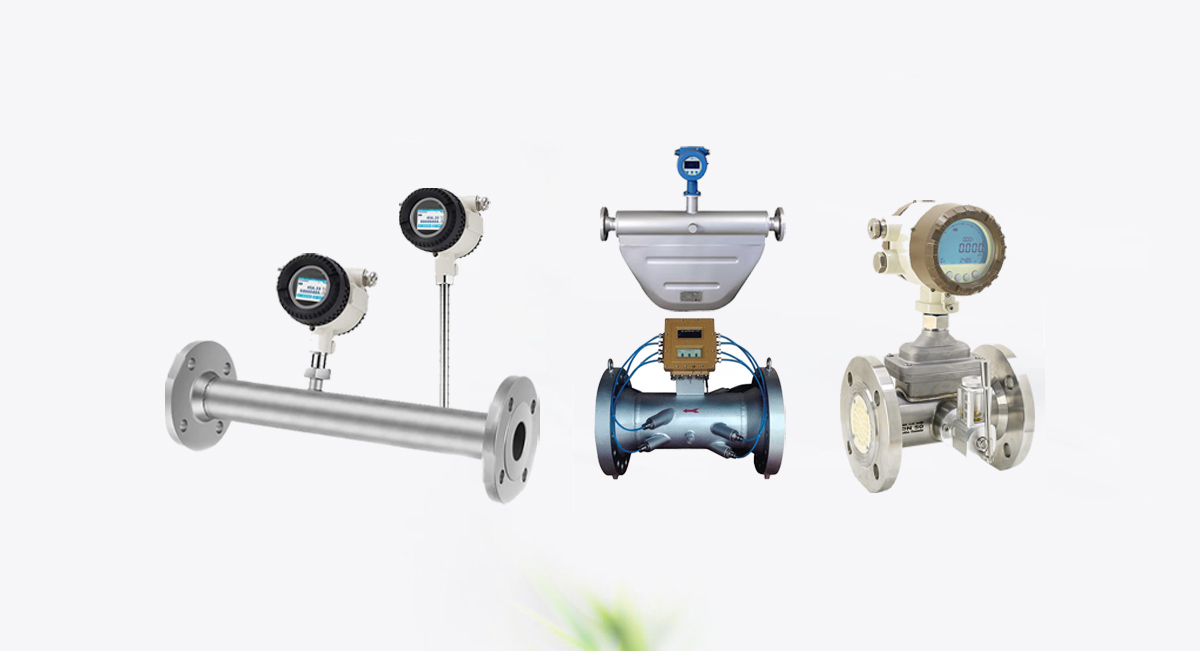
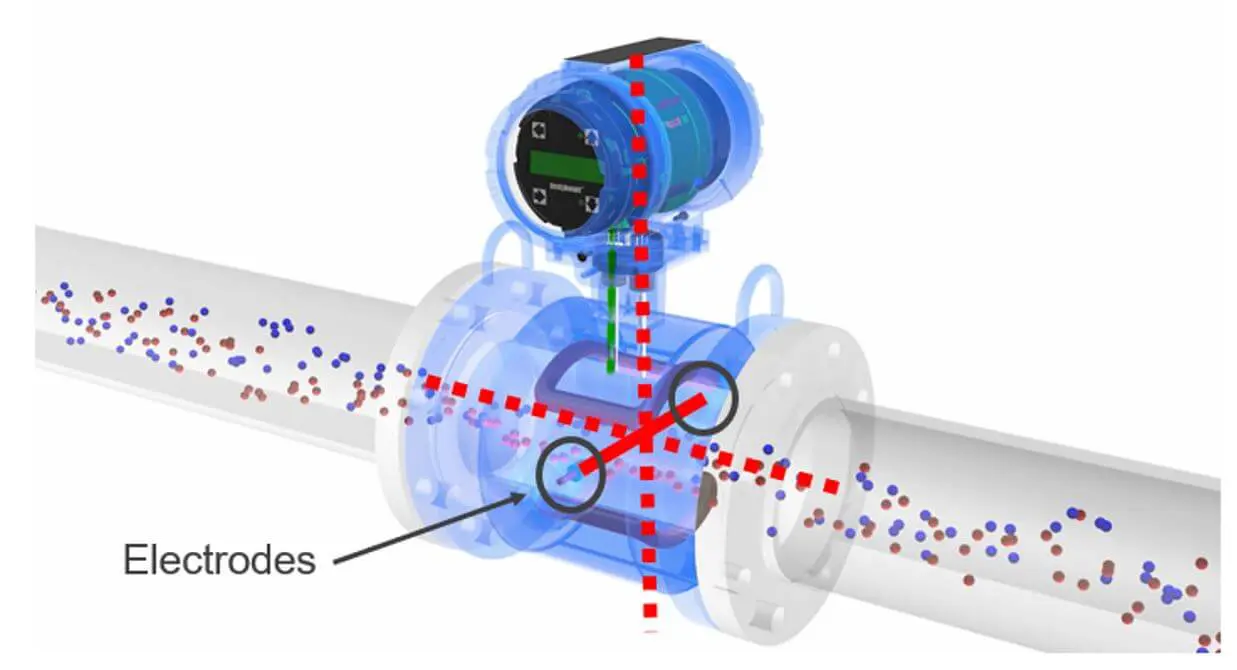
1. Débitmètres électromagnétiques
Principe de fonctionnement :
Débitmètres électromagnétiques operate on the principle of Faraday’s Law of Induction, which states that a voltage is induced when a conductor moves through a magnetic field. In the case of an electromagnetic flow meter, the fluid acts as the conductor. The meter generates a magnetic field in the flow tube, and as the conductive fluid (e.g., water, slurry, or chemicals) flows through it, a voltage is induced. This voltage is directly proportional to the flow rate, and the flow meter measures it to calculate the volumetric flow.
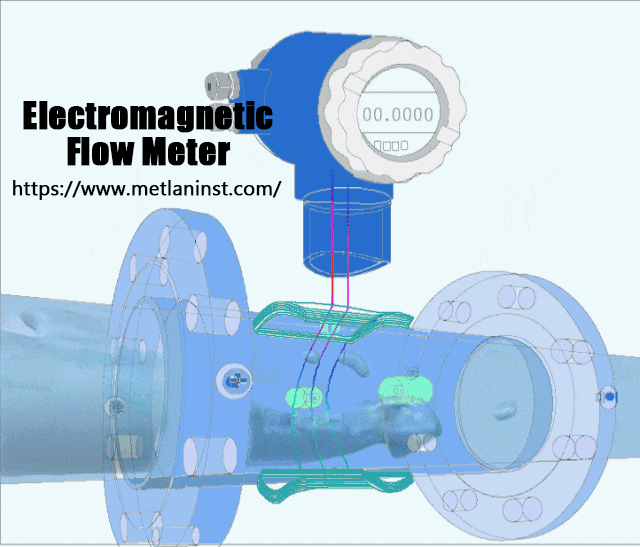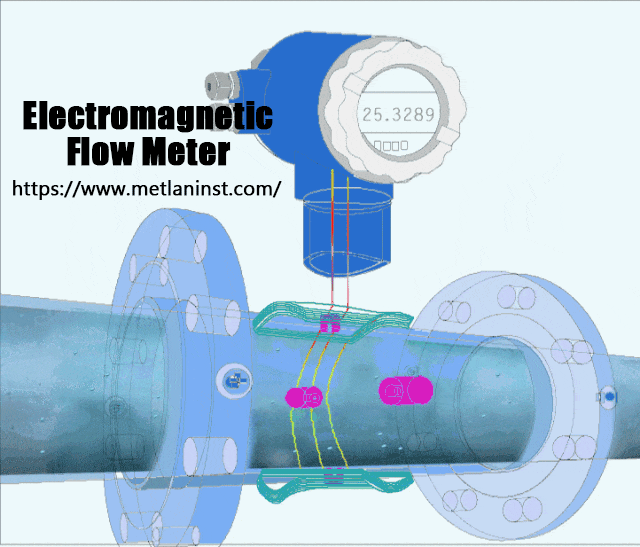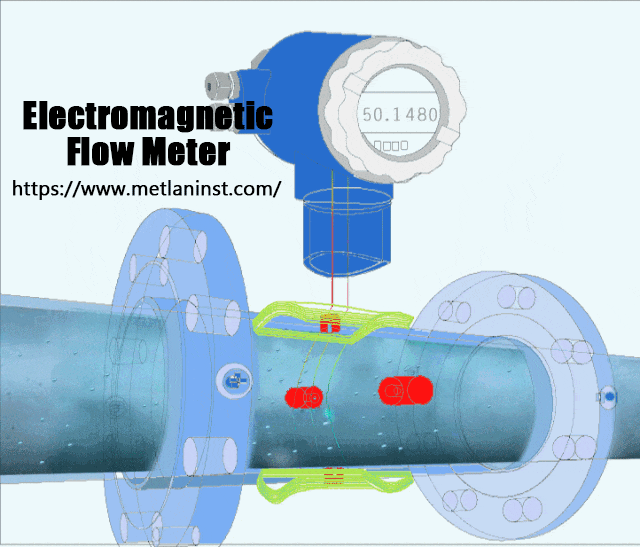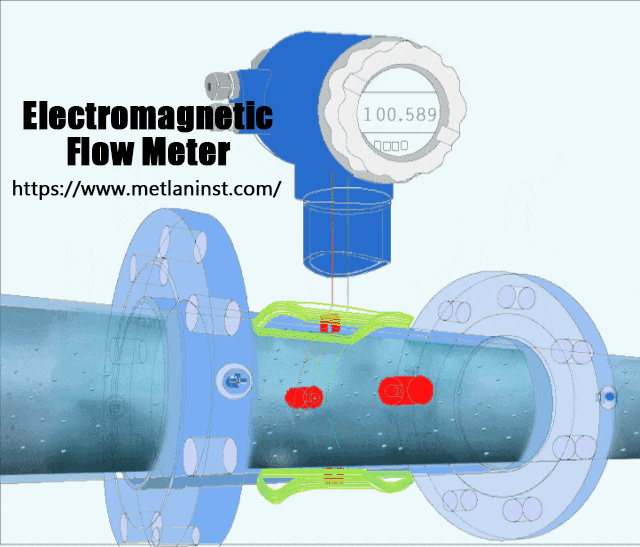
Avantages :
- Très précis pour les liquides conducteurs.
- Aucune pièce mobile, ce qui réduit l'usure et les besoins de maintenance.
- Fonctionne bien pour les liquides sales ou abrasifs.
- Convient à un large éventail d'industries telles que le traitement de l'eau, l'alimentation et les boissons, et le traitement chimique.
Limites :
- Le fluide doit être conducteur (par exemple, l'eau, les acides ou les boues).
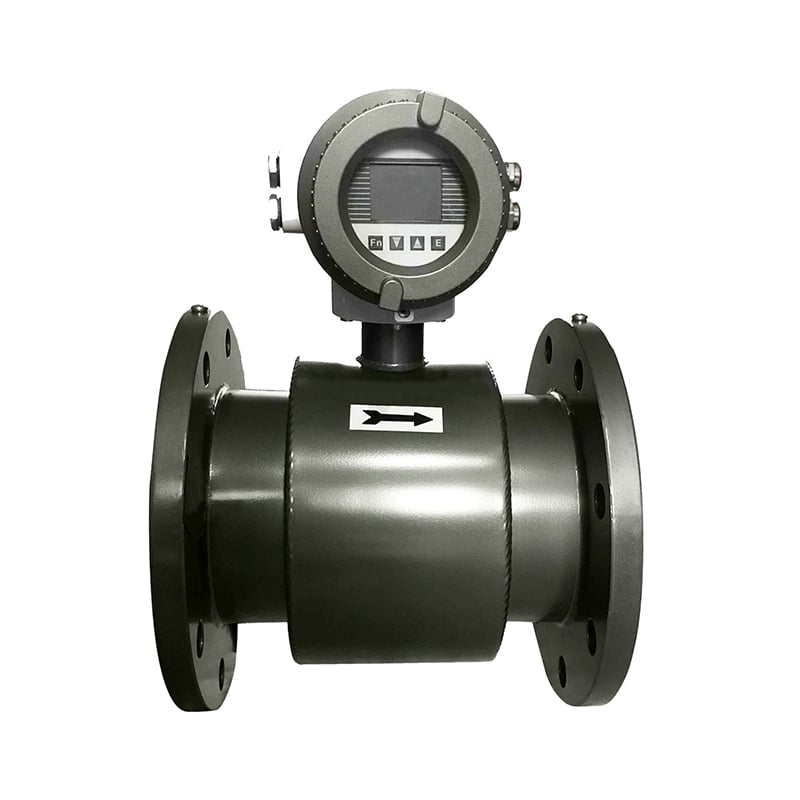

Caractéristiques :
- Revêtement en PU, PFA, ETFE ou FEP : excellente résistance aux produits chimiques et à l'abrasion.
- Large gamme de matériaux d'électrodes
- Les couleurs et l'aspect peuvent être personnalisés sur demande
- Également disponible dans des constructions spécifiques au client
- Pas de pièces mobiles, pas d'usure, pas de perte de pression
- Mesures fiables avec une précision constante
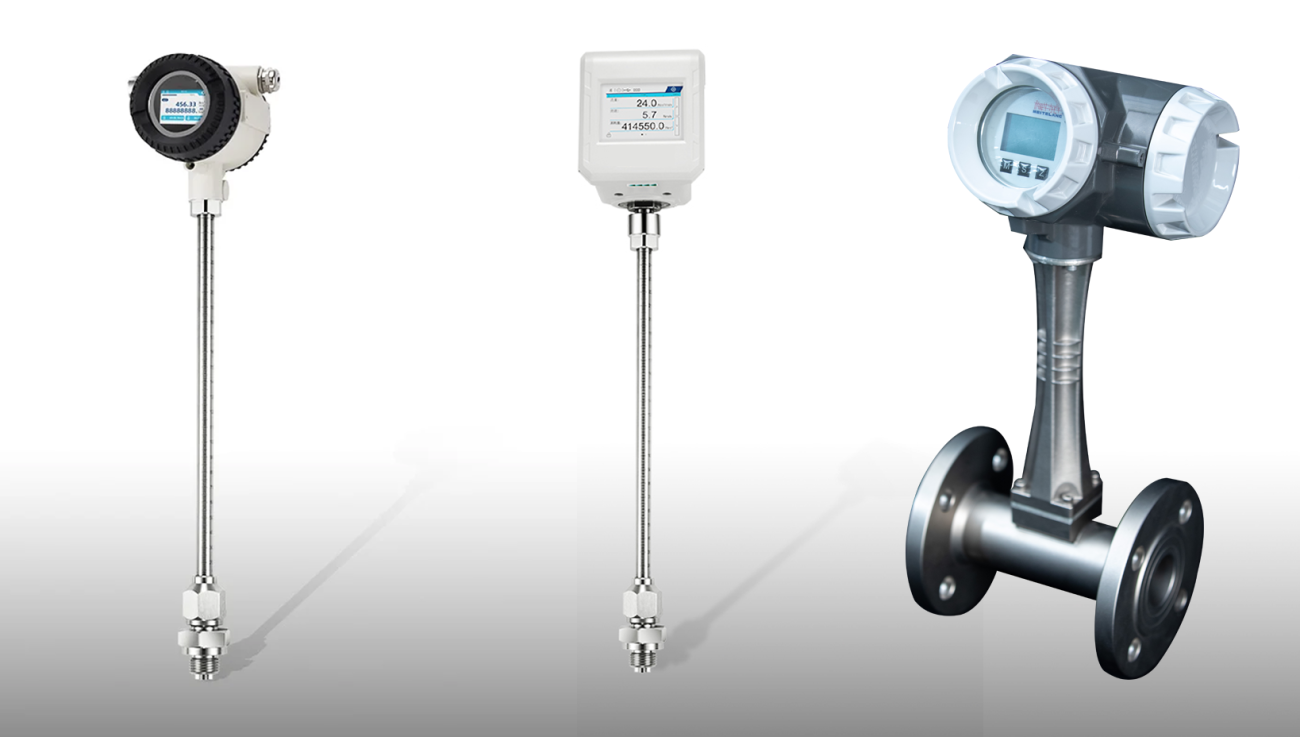
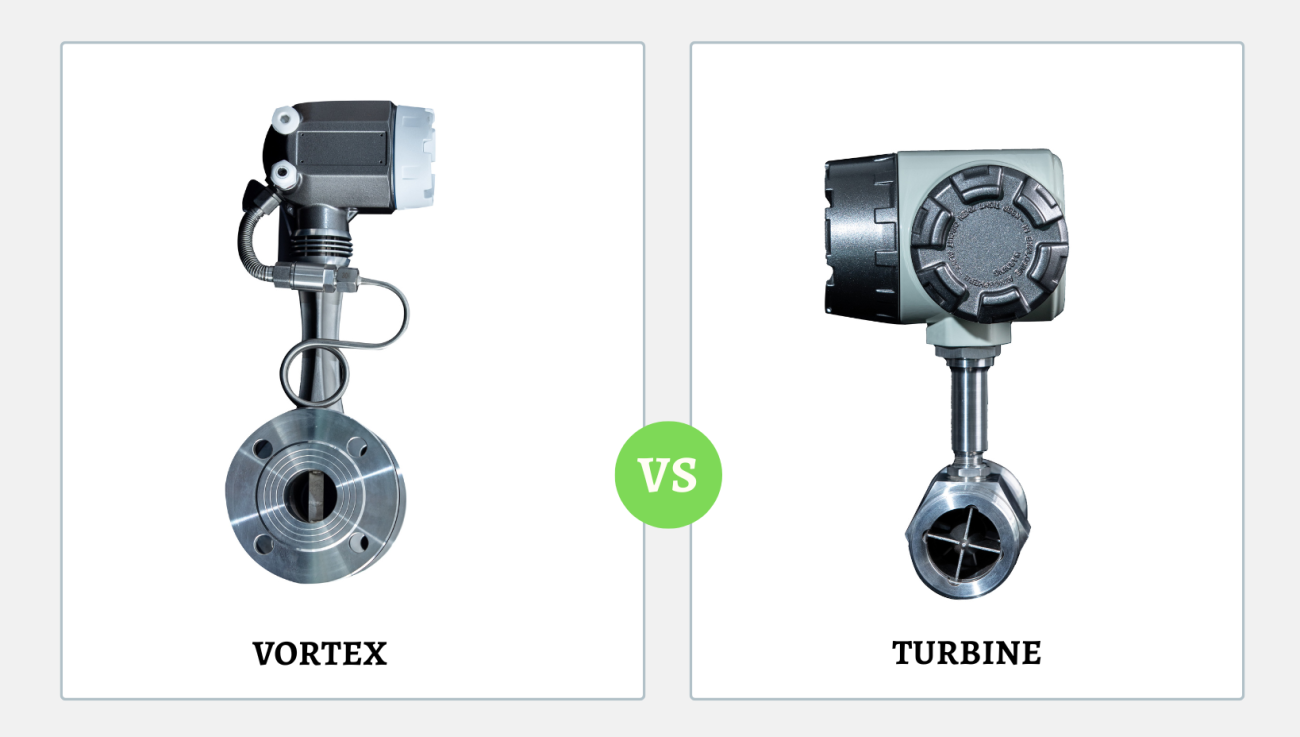
2. Débitmètres à turbine
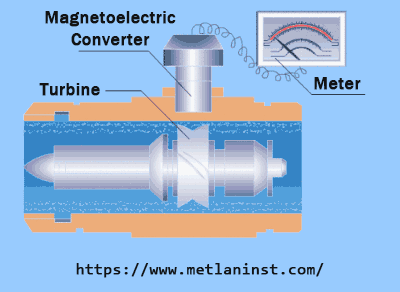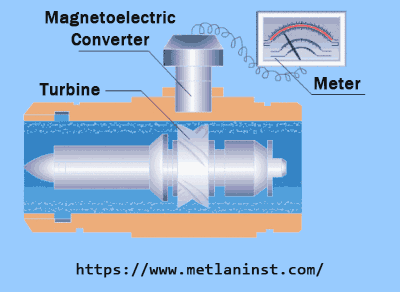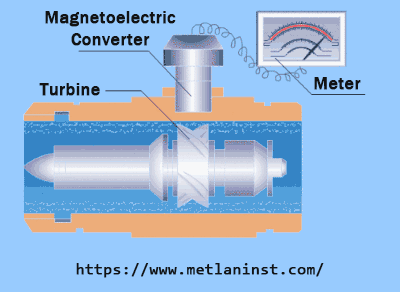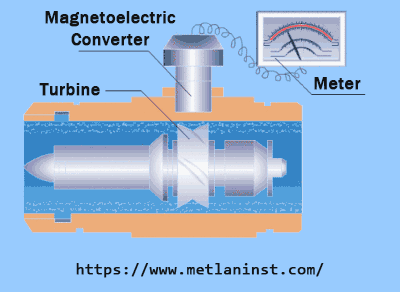
Principe de fonctionnement :
Les débitmètres à turbine mesurent le débit en détectant la vitesse de rotation d'une turbine placée dans le circuit d'écoulement du fluide. Lorsque le fluide traverse le compteur, il fait tourner les pales de la turbine. La vitesse de rotation de la turbine est directement proportionnelle à la vitesse du fluide. En connaissant la section transversale de la conduite et la vitesse de rotation de la turbine, il est possible de calculer le débit volumétrique.
Avantages :
- Haute précision pour les fluides propres et de faible viscosité.
- Idéal pour les applications dans les industries pétrolières et gazières, pharmaceutiques et alimentaires.
- Conception relativement simple et rentable pour de nombreuses applications.
Limites :
- Ne convient pas aux fluides à haute viscosité ou aux boues en raison du risque d'endommagement de la turbine.
- La précision peut être affectée par des changements de température ou de pression du fluide.
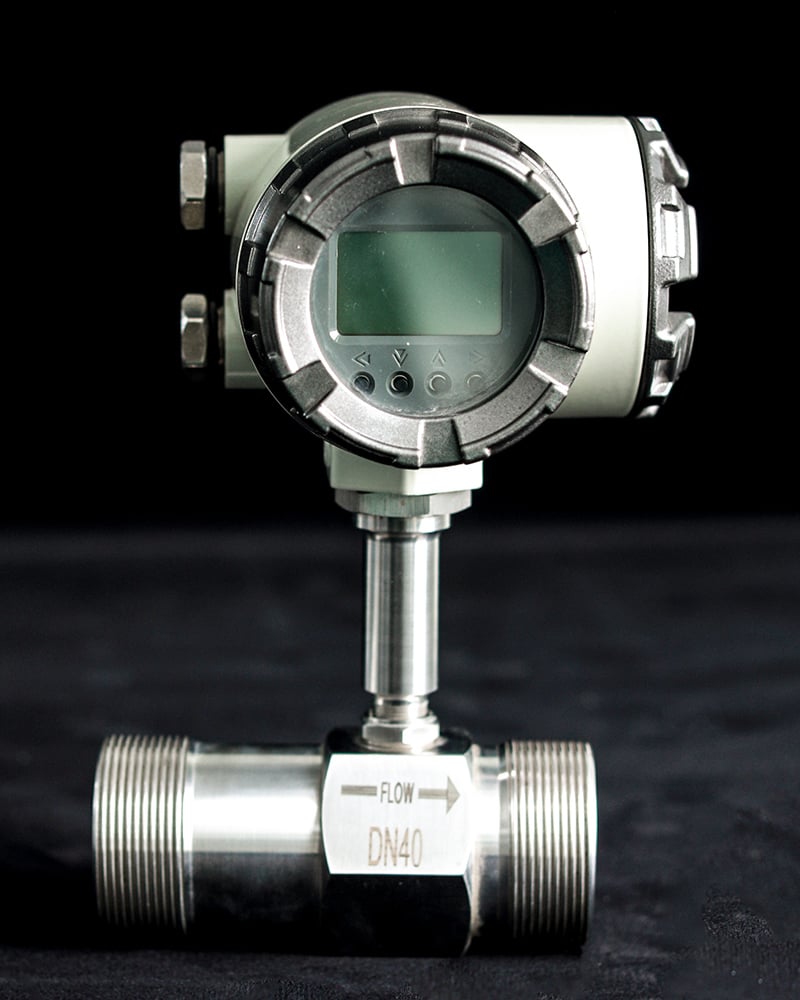

Caractéristiques :
- Spécialement conçu pour les applications à faible débit
- Les couleurs et l'aspect peuvent être personnalisés sur demande
- Également disponible dans des constructions spécifiques au client
- L'anglais, l'espagnol, le français et d'autres langues sur demande sont disponibles pour l'affichage LCD.
- Chaque débitmètre est étalonné et reçoit un numéro de série unique correspondant à toutes les données d'étalonnage.
3. Débitmètres à déplacement positif
Principe de fonctionnement :
Les débitmètres à déplacement positif fonctionnent en capturant un volume connu de fluide et en comptant combien de fois ce volume est déplacé lorsque le fluide s'écoule à travers le compteur. Ces compteurs utilisent généralement des chambres ou des pistons qui se remplissent et se vident de fluide à chaque cycle, ce qui permet au compteur de mesurer directement le débit volumétrique.
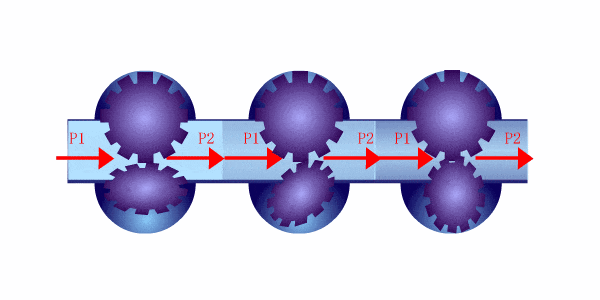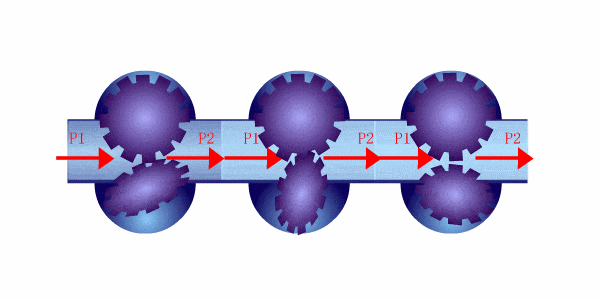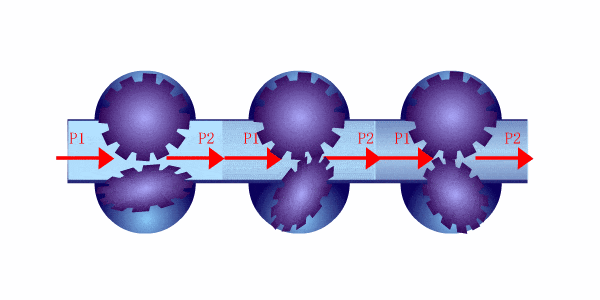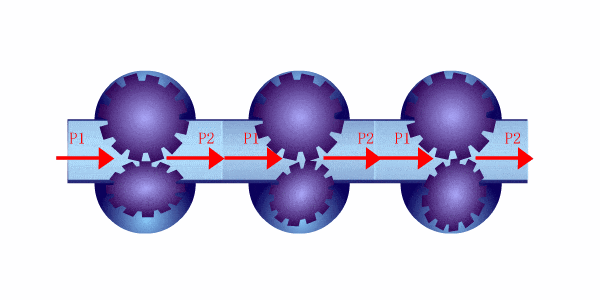
Parmi les types courants de débitmètres à déplacement positif figurent les compteurs à piston rotatif, les compteurs à engrenage et les compteurs à diaphragme. Chaque modèle implique un mécanisme qui retient un volume précis de fluide et mesure le nombre de fois qu'il déplace ce volume pour calculer le débit.
Avantages :
- Extrêmement précis, en particulier pour les faibles débits.
- Mesure le débit volumétrique réel, indépendamment des propriétés du fluide telles que la pression, la température ou la viscosité.
- Peut traiter une grande variété de fluides, y compris les huiles, les produits chimiques et les liquides à haute viscosité.
Limites :
- Des pièces mécaniques qui peuvent s'user avec le temps, d'où la nécessité d'un entretien régulier.
- Ne convient pas aux débits très élevés ni aux fluides contenant des solides en suspension.
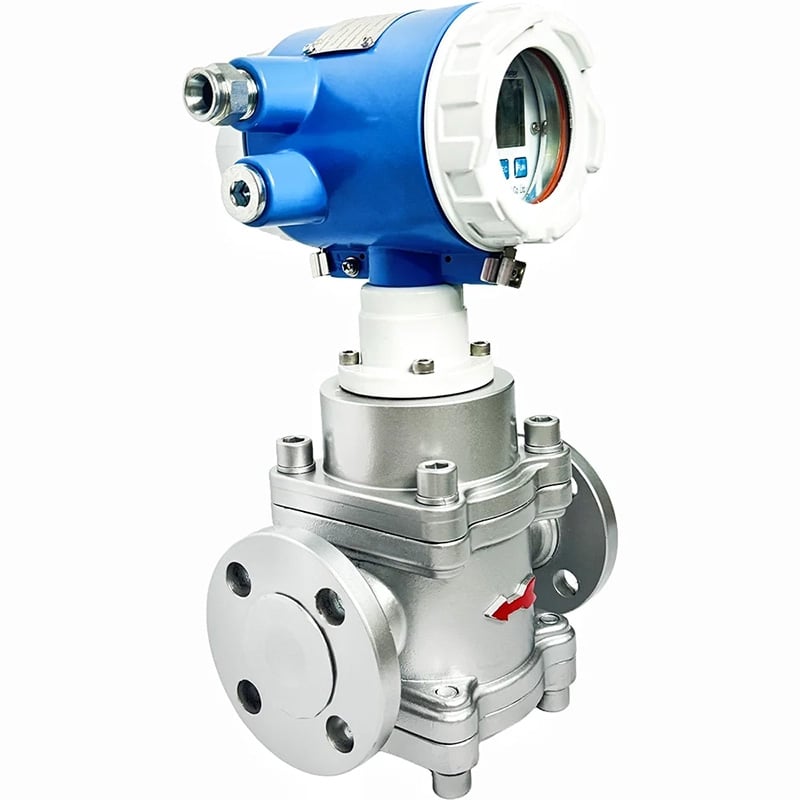

Caractéristiques :
- Haute précision jusqu'à ±0,1 %, haute pression de processus jusqu'à 110 bar (1595 psi)
- Stabilité dans la course à voix basse
- Bonne performance anti-interférence et longue durée de vie
- Forte applicabilité aux changements de viscosité
- Également disponible dans une construction spécifique au client
- Chaque débitmètre est étalonné et reçoit un numéro de série unique correspondant à toutes les données d'étalonnage.
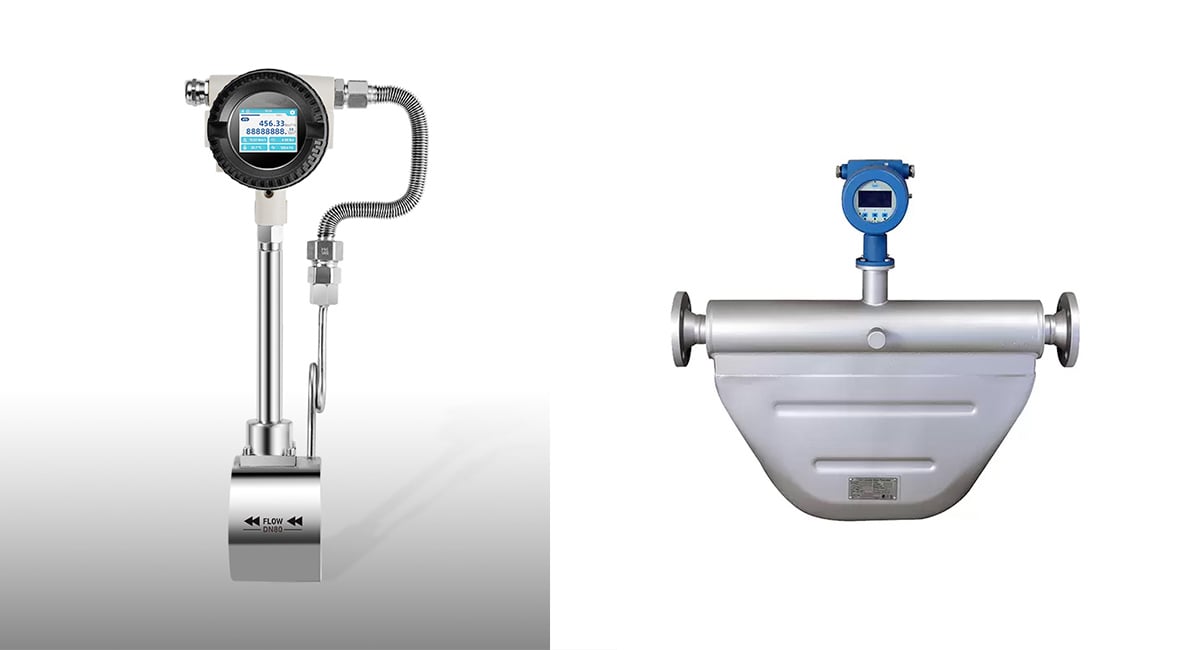
4. Débitmètres à vortex
Principe de fonctionnement :
Les débitmètres à tourbillon fonctionnent selon le principe de la rue tourbillonnaire de Kármán, où le fluide passant au-dessus d'un corps de falaise (un obstacle cylindrique ou rectangulaire sur la trajectoire de l'écoulement) crée des tourbillons de part et d'autre du corps. La fréquence des tourbillons est proportionnelle à la vitesse de l'écoulement. En mesurant la fréquence des tourbillons, le compteur peut calculer le débit volumétrique du fluide.
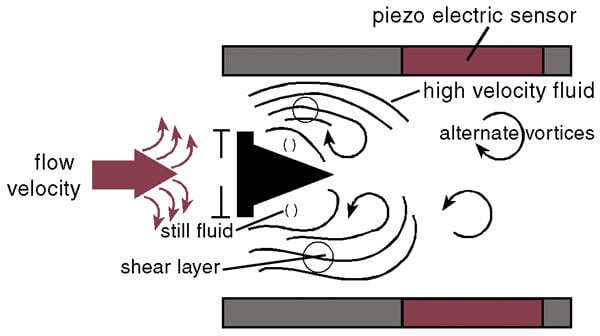
Ces compteurs utilisent souvent des capteurs tels que des cristaux piézoélectriques ou des transducteurs ultrasoniques pour détecter les tourbillons et convertir les données en une mesure précise du débit.
Avantages :
- Peut mesurer les liquides et les gaz.
- Il n'y a pas de pièces mobiles, ce qui réduit l'entretien.
- Il permet d'obtenir un débit propre et stable avec des fluides de viscosité relativement faible à modérée.
- Convient à une large gamme d'applications industrielles telles que la surveillance des débits de vapeur, de gaz et de liquides.
Limites :
- Il n'est pas idéal pour les faibles débits en raison de la difficulté à détecter la fréquence des tourbillons.
- Peut être affecté par des changements de viscosité ou de densité du fluide.
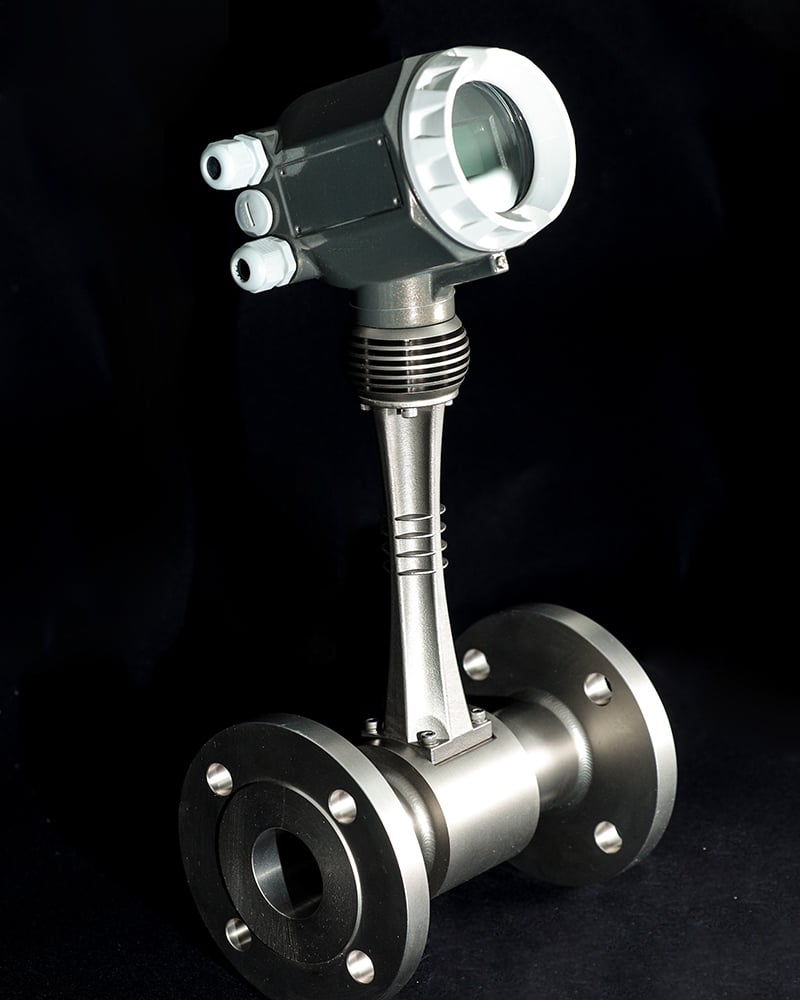

Caractéristiques :
- Pour les applications à haute température jusqu'à +400°C / +750°F
- Les couleurs et l'aspect peuvent être personnalisés sur demande
- Également disponible dans des constructions spécifiques au client
- L'anglais, l'espagnol, le français et d'autres langues sur demande sont disponibles pour l'affichage LCD.
- Chaque débitmètre est étalonné et reçoit un numéro de série unique correspondant à toutes les données d'étalonnage.
5. Débitmètres à ultrasons
Principe de fonctionnement :
Les débitmètres à ultrasons utilisent des ondes sonores pour mesurer le débit des fluides. Il en existe deux types principaux : temps de transit et Doppler les compteurs à ultrasons.
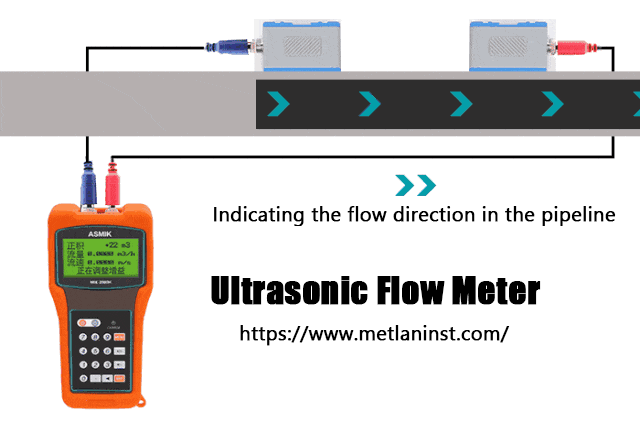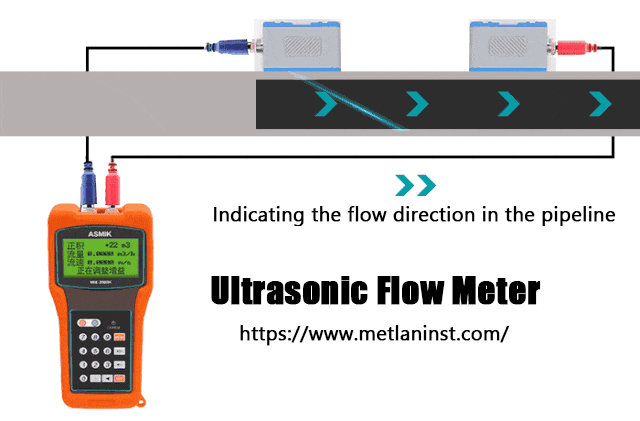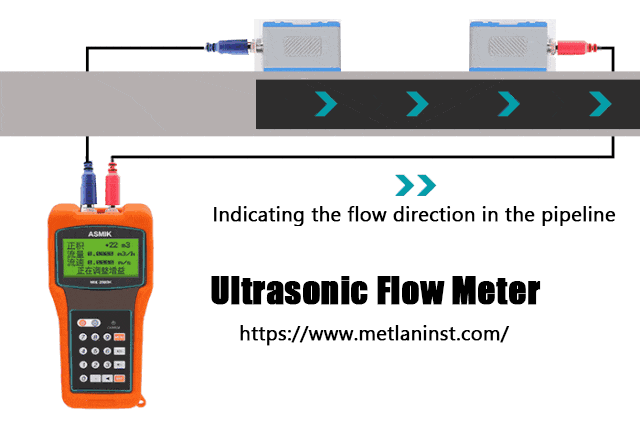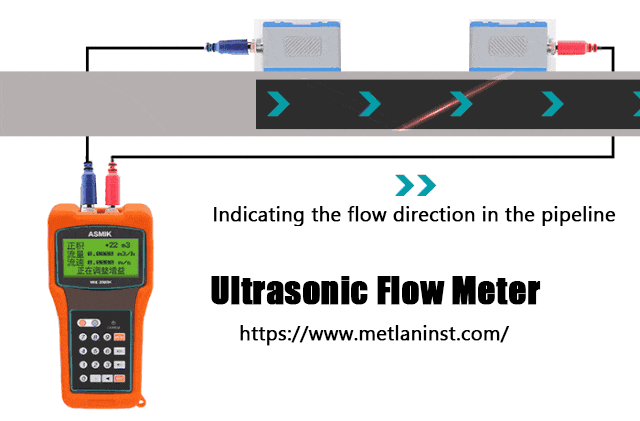
- Compteurs à ultrasons à temps de transit fonctionnent en envoyant des signaux ultrasoniques en amont et en aval du fluide. La différence de temps nécessaire aux ondes sonores pour se déplacer dans chaque direction est utilisée pour calculer la vitesse d'écoulement, ce qui permet d'obtenir le débit volumétrique.
- Compteurs à ultrasons Doppler mesurent le décalage de fréquence des ondes sonores réfléchies par les particules ou les bulles dans le fluide. Ce décalage fournit des données sur la vitesse d'écoulement et permet de calculer le débit.
Avantages :
- Ils ne comportent pas de pièces mobiles et ne nécessitent donc pratiquement pas d'entretien.
- Non intrusifs, car ils peuvent être installés à l'extérieur de la canalisation.
- Convient à une large gamme de fluides, y compris les liquides propres et sales, les boues et les gaz.
- Très précis, en particulier dans des applications telles que le traitement de l'eau, les gazoducs et les usines chimiques.
Limites :
- Les compteurs de temps de transit ont besoin d'un fluide propre et homogène pour obtenir des relevés précis.
- Ils peuvent être plus chers que d'autres types de débitmètres.
- Limité par la taille du tube et l'épaisseur de la paroi dans certains cas.
Comment choisir le bon débitmètre volumétrique ?
Le choix du bon débitmètre volumétrique dépend de plusieurs facteurs, notamment des caractéristiques du fluide, de la précision requise, de l'environnement de fonctionnement et de l'application spécifique. Vous trouverez ci-dessous quelques considérations clés pour vous aider à choisir le débitmètre le mieux adapté à vos besoins.
1. Type et propriétés des fluides
- Viscosité: Les fluides à haute viscosité peuvent ne pas s'écouler facilement dans certains compteurs tels que les compteurs à turbine ou à vortex. Débitmètres à déplacement positifsont idéales pour de tels fluides.
- Conductivité: Pour débitmètres électromagnétiquesLe fluide doit être conducteur (comme l'eau ou les acides). Les fluides non conducteurs nécessitent un autre type de débitmètre.
- Solides en suspension: Si le fluide contient des particules ou des solides, un débitmètre à déplacement positif ou un débitmètre à ultrasons (en fonction de la nature du solide) serait un meilleur choix.
2. Plage de débit
- Si vous devez mesurer à la fois des débits très faibles et très élevés, choisissez un débitmètre ayant une large plage de débit, comme les compteurs à ultrasons.
3. Exigences de précision
- Pour les applications exigeant une grande précision, débitmètres à déplacement positif sont souvent le meilleur choix en raison de leur mesure volumétrique directe. Pour des besoins de moindre précision, un vortex ou turbine peut suffire.
4. Entretien et durabilité
- Si vous êtes à la recherche d'une solution nécessitant peu d'entretien, envisagez une vortex, ultrasoniqueou débitmètre électromagnétiquequi n'ont pas de pièces mobiles.
- Pour les conditions difficiles ou la manipulation de fluides, les compteurs à déplacement positif ou les compteurs à turbine conviennent mieux, mais il faut garder à l'esprit que leurs composants mécaniques peuvent nécessiter une maintenance au fil du temps.
5. Environnement de l'application
- Pression et température de fonctionnement: Assurez-vous que le débitmètre choisi peut supporter les plages de température et de pression typiques de votre procédé.
- Espace d'installation: Certains débitmètres, comme les débitmètres à ultrasons ou électromagnétiques, peuvent être mieux adaptés aux espaces d'installation restreints, car ils peuvent parfois être installés à l'extérieur.
Les débitmètres volumétriques sont des outils indispensables pour de nombreuses industries, car ils offrent des mesures précises et fiables du débit des fluides. Qu'il s'agisse d'eau, de produits chimiques, d'huiles ou de gaz, le choix du bon type de débitmètre volumétrique - qu'il s'agisse d'un débitmètre à piston ou d'un débitmètre à piston - est essentiel. électromagnétique, turbine, déplacement positif, vortexou débitmètre à ultrasons-dépend de la compréhension des caractéristiques uniques de votre application et de votre fluide.
En examinant attentivement les propriétés du fluide, la plage de débit, les exigences de précision et les conditions environnementales, vous pouvez sélectionner le meilleur débitmètre volumétrique pour garantir des performances optimales, l'efficacité et la longévité de vos opérations.







Laisser un commentaire