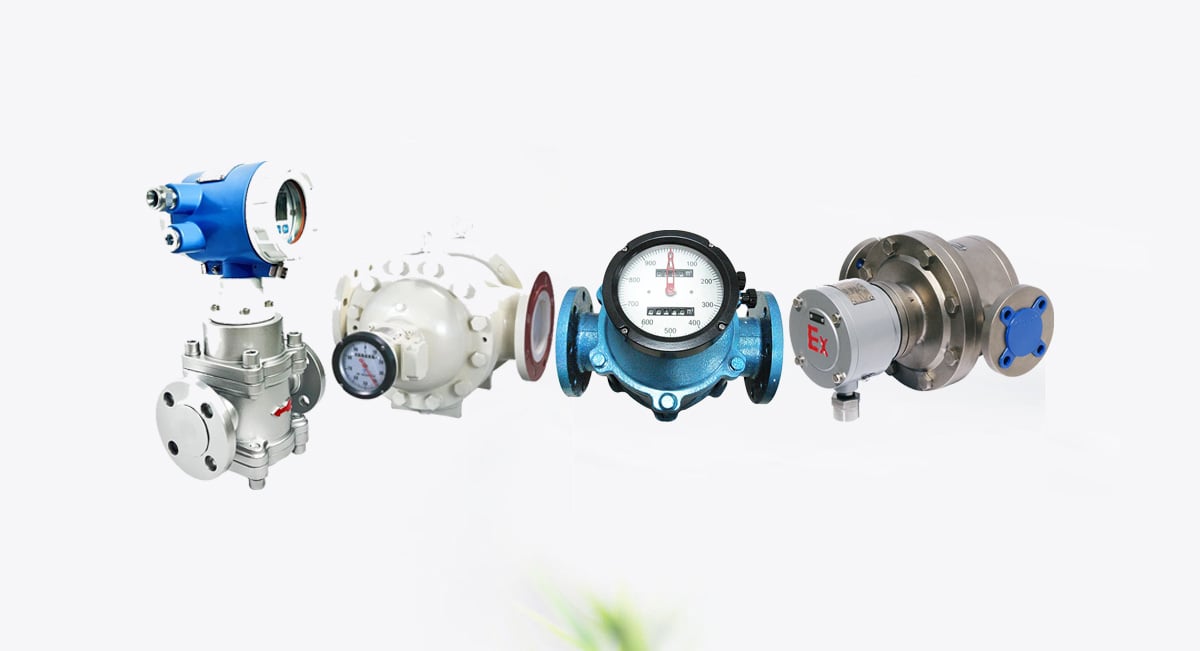
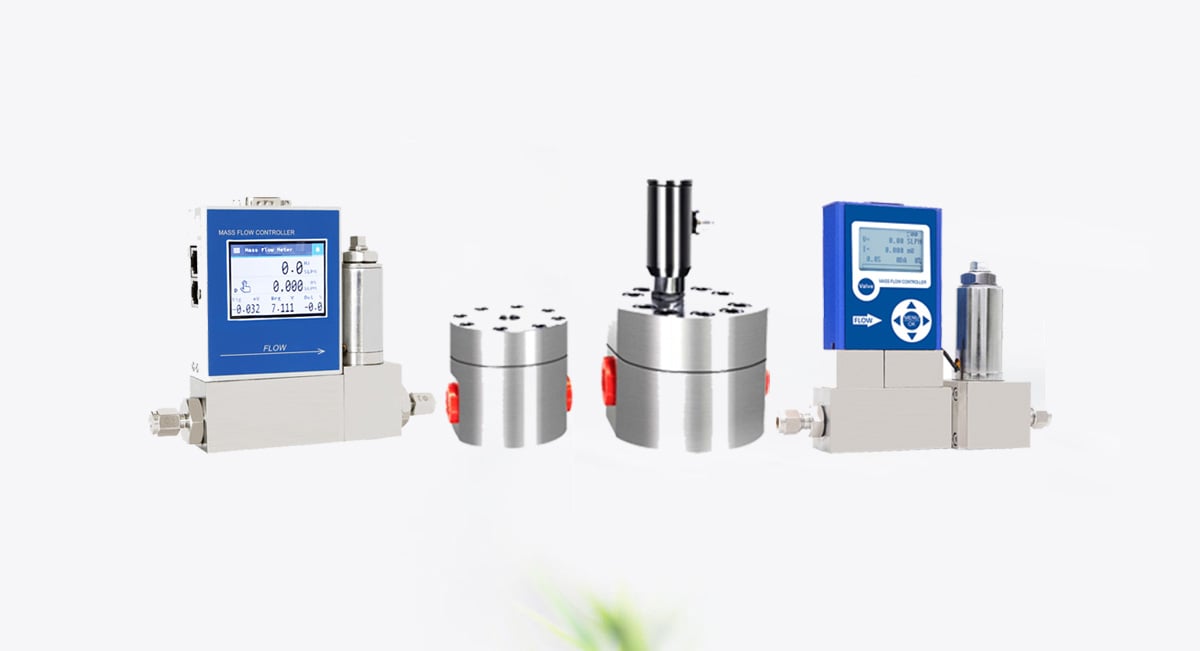
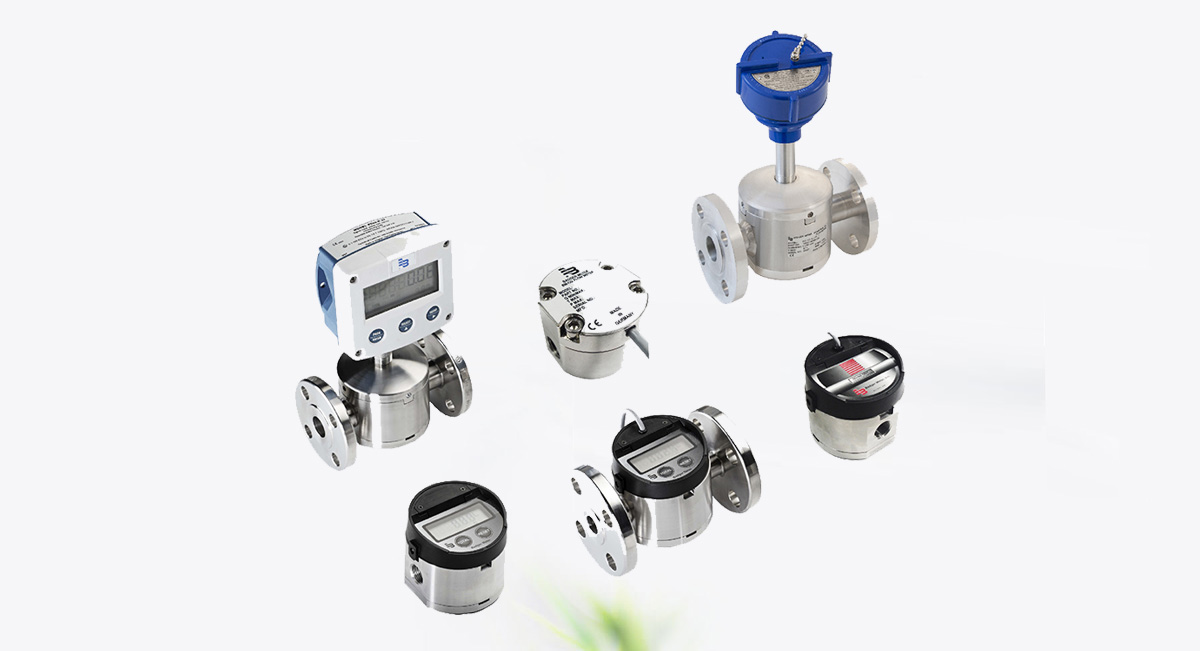
When it comes to measuring the flow of liquids—especially those with high viscosity or at low flow rates—positive displacement (PD) flow meters offer unmatched precision and reliability. From chemical batching to oil metering, these robust instruments provide volumetric accuracy where other flow technologies may fail.
Table des matières
What Is a Positive Displacement Flow Meter?
A débitmètre volumétrique is a volumetric flow measurement device that directly counts the volume of liquid passing through it. Unlike other flow meters that infer flow based on velocity, pressure drop, or thermal properties, PD flow meters physically trap and release precise volumes of fluid, ensuring high-accuracy measurement.
They are particularly well-suited for:
- High-viscosity liquids (like crude oil, honey, or glue)
- Low flow rate conditions
- Applications requiring totalization (batching, dispensing, blending)
Positive displacement meters are often regarded as mechanical counters—each rotation, oscillation, or movement corresponds to a fixed volume of fluid, enabling accurate totalization without the need for complex calculations.
How Does a Positive Displacement Flow Meter Work?
At the core of every PD meter is a chamber et mechanical components (e.g., gears, pistons, rotors) that rotate or move to trap a fixed volume of fluid. Each cycle of movement corresponds to a known, consistent volume. By counting these cycles, the meter calculates total volume et débit.
Here’s a simplified process of how it works:
- Fluid Enters the Meter The incoming fluid is directed into the measuring chamber.
- Mechanical Displacement Internal rotating or oscillating components (e.g., gears, disks, pistons) trap a fixed volume of fluid.
- Fluid Discharge As the chamber moves, the fluid is pushed out and exits the meter.
- Volume Counting Each movement is detected by sensors or magnets, and the cumulative count represents the total volume passed.
Because the meter measures flow volumetrically, its accuracy is largely unaffected by changes in fluid properties such as viscosity, density, or turbulence—making it ideal for precise, repeatable measurement in challenging conditions.
Types of Positive Displacement Flow Meters
There are several different types of PD flow meters, each suited for different flow rates, fluid types, and applications. Here are the most commonly used varieties:
1. Gear Flow Meters
Comment ils fonctionnent :
Gear flow meters use two intermeshing gears—typically oval or helical—to form pockets of fluid that are moved from the inlet to the outlet.
Meilleur pour :
- High-viscosity liquids (oil, glue, syrup)
- Low flow conditions
- Precise dispensing
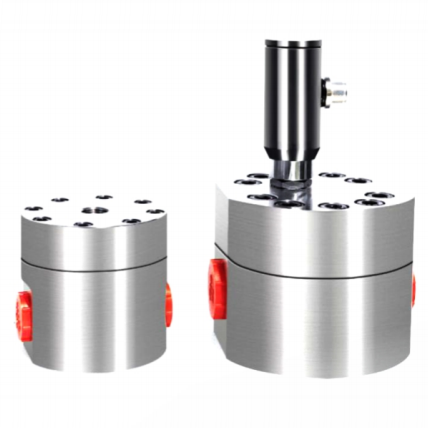

- Conçu pour les liquides à faible débit à partir de 0,6 L/H
- Rapport de réduction large de 150:1
- Capable de mesurer des milieux très corrosifs, y compris l'acide sulfurique, l'acide fluorhydrique et d'autres produits chimiques agressifs.
- Conçue pour la mesure de fluides à haute viscosité, elle permet de traiter des fluides difficiles tels que le sirop, l'asphalte fondu et le miel avec une précision fiable.
- Mesures de haute précision jusqu'à ±0,5%
2. Rotary Vane Flow Meters
Comment ils fonctionnent :
A rotor with multiple vanes turns inside a cylindrical housing. Each rotation traps a known volume of liquid and transfers it through the meter.
Meilleur pour :
- Water-based fluids
- Heating oil and fuel
- Industrial process flows
3. Piston Flow Meters
Comment ils fonctionnent :
Fluid is drawn into and pushed out of chambers by oscillating or rotating pistons. Each stroke displaces a fixed volume.
Meilleur pour :
- Clean, low-viscosity fluids
- Injection de produits chimiques
- Pharmaceutical and medical dosing
4. Nutating Disk Flow Meters
Comment ils fonctionnent :
A disk mounted on a central ball “wobbles” (nutates) inside a chamber, displacing fluid in fixed volumes per cycle.
Meilleur pour :
- Residential water meters
- Beverage dispensing
- Custody transfer systems
5. Bi-Rotor Flow Meters
Comment ils fonctionnent :
Two rotors rotate inside a cavity, creating fluid pockets that are displaced through the meter. These meters have minimal internal friction, making them ideal for sanitary applications.
Meilleur pour :
- Food-grade fluids
- Produits pharmaceutiques
- Viscous fluids like oil, resin, or syrup
- Custody transfer systems
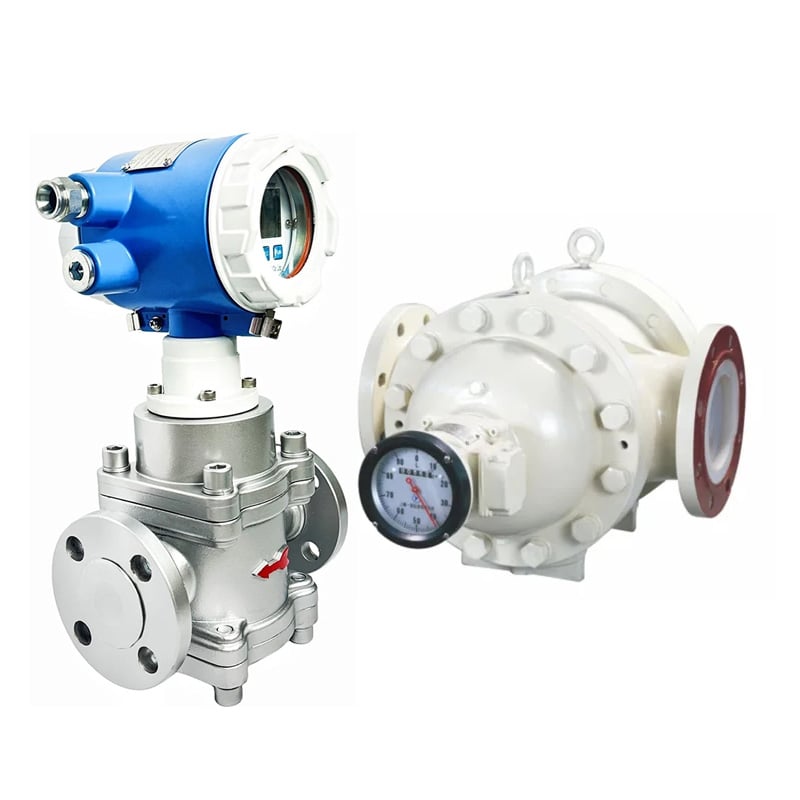

- Haute précision jusqu'à ±0,1 %, haute pression de processus jusqu'à 110 bar (1595 psi)
- Durée de vie extrêmement longue, entretien réduit et économique
- Aucune pièce oscillante, alternative ou coulissante, ni aucune manivelle n'est susceptible d'user ou de perturber l'équilibre rotatif.
- Stabilité dans la course à voix basse
- Bonne performance anti-interférence et longue durée de vie
- Forte applicabilité aux changements de viscosité
6. Oval Gear Débitmètres
Comment ils fonctionnent :
Oval gear meters use two interlocking oval-shaped gears that rotate with the flow of fluid. Each rotation displaces a known volume, and the number of rotations is proportional to the total volume passed through.
Meilleur pour :
- Viscous fluids like oil, resin, or syrup
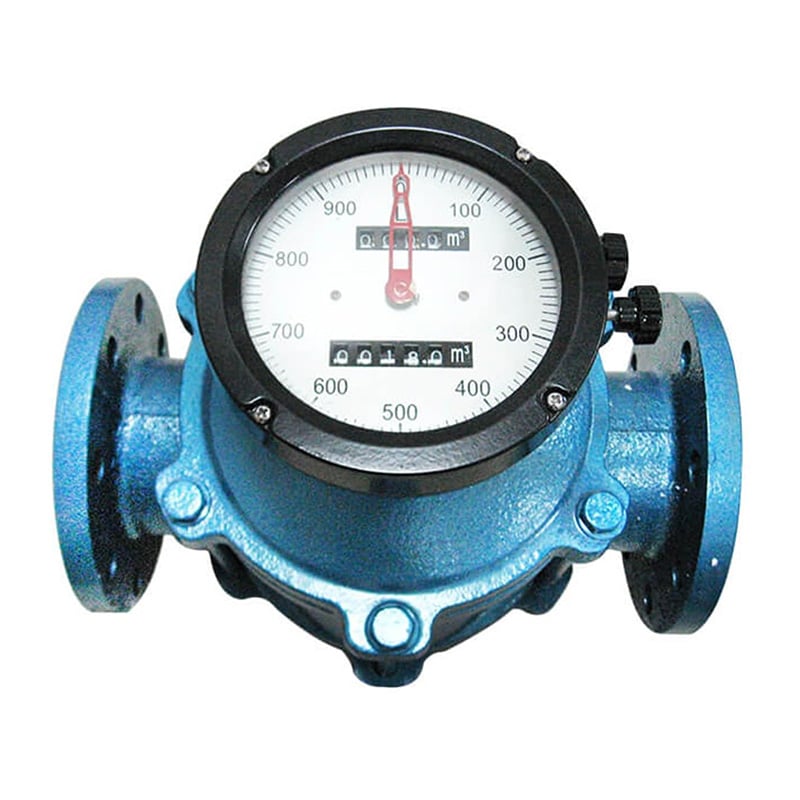

- Fonctionnement régulier du rotor en spirale avec un minimum de vibrations pour des performances constantes
- Large plage de mesure avec une bonne répétabilité
- Mesures de haute précision jusqu'à ±0,2%
- Insensible au changement de viscosité
- Optimisé pour la mesure des liquides à haute viscosité
- Installation simple ne nécessitant pas de tuyaux droits
Avantages des débitmètres à déplacement positif
Positive displacement flow meters offer many performance and operational advantages, making them the go-to solution in applications where accuracy and repeatability are critical.
- Direct Measurement of Volume: They don’t estimate or infer—PD meters measure the actual fluid volume passing through, which eliminates many common sources of error.
- High Accuracy at Low Flow Rates: They are among the most accurate flow meters at very low flow levels, which makes them ideal for dosing and micro-batching applications.
- Insensible aux propriétés du fluide:PD meters are not affected by fluid density, viscosity, or temperature to the extent that other technologies are.
- No Need for Straight Pipe Runs: Unlike turbine or ultrasonic meters, PD meters don’t require long upstream or downstream pipe lengths, which is a major benefit in compact installations.
- Excellent Repeatability: Their mechanical design ensures highly consistent performance over time.
- Totalizing and Batch-Friendly: Perfect for batching, filling, or blending systems where cumulative volume matters.
Disadvantages of Positive Displacement Flow Meters
While PD flow meters offer numerous benefits, there are some limitations to consider when choosing this technology.
- Not Ideal for Dirty Fluids: Solids, debris, or particulates can damage internal moving parts or cause clogging.
- Mechanical Wear and Tear: Over time, mechanical components can wear down, especially if proper filtration or maintenance is not observed.
- Size and Cost at High Flow Rates: For high-flow applications, PD meters become bulky and expensive compared to other technologies.
Recommended Fluids and Mediums for PD Flow Meters
Positive displacement flow meters work best with clean, viscous, and incompressible liquids. Here are common media types that are well-suited for PD technology:
Oils
- Hydraulic oil
- Lubricating oil
- Engine oil
- Pétrole brut
Produits chimiques
- Resins and adhesives
- Solvants
- Additives and catalysts
Alimentation et boissons
- Honey
- Syrup
- Flavor concentrates
- Milk and dairy products
Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic
- Glycerin
- Alcohol-based fluids
- Emulsions
- Liquid medication
Applications des compteurs à déplacement positif Débitmètres
Thanks to their accuracy and reliability, PD flow meters are used in a variety of industries and processes. Here are some of the most common use cases:
1. Chemical Injection and Dosing
In water treatment, oil refining, and specialty chemical manufacturing, PD meters ensure precise injection of expensive or reactive chemicals.
2. Oil and Fuel Measurement
They are widely used in lube oil blending plants, diesel fuel transfer systems, and engine testing labs to measure and totalize fuel flow.
3. Food and Beverage Processing
In high-viscosity food products such as honey or syrups, PD meters ensure consistent dosing during filling and packaging.
4. Cosmetics and Personal Care
PD meters accurately dispense lotions, creams, and gels in controlled environments.
5. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
For high-value drugs and bio-fluids, PD meters are used in ultra-precise filling, mixing, and formulation applications.
6. Paints and Coatings
In pigment and resin applications, PD meters help maintain proper ratios and minimize waste.
Explore Metlan’s PD Flow Meter Solutions
Au Metlan Instruments, we offer industry-grade positive displacement flow meters tailored for low flow, high-viscosityet precision-critical des applications.
Need help finding the right meter for your system? Contact us today—we’ll help you select the perfect solution for your application.