In the chemical and process industries, accurate measurement and control of fluid flow are fundamental to ensuring product quality, safety, and efficiency. Chemicals often vary widely in viscosity, corrosiveness, temperature, and pressure — making flow measurement a technical challenge that requires specialized instruments.
Table des matières
What Is a Chemical Flow Meter?
A chemical flow meter is an instrument designed to measure the rate or total volume of chemical fluids passing through a pipeline. These fluids can include liquid chemicals, corrosive acids, alkalis, solvents, fuels, and even chemical gases.
The purpose of a chemical flow meter is to ensure that precise quantities of chemicals are delivered, mixed, or reacted as required in industrial processes. Accurate flow measurement is critical in sectors such as:
- Chemical manufacturing (acid/base dosing, solvent blending)
- Pharmaceutical production (precise ingredient ratios)
- Petrochemical and refinery processes (fuel and lubricant monitoring)
- Water and wastewater treatment (chlorine or pH-control chemicals)
- Industrie alimentaire et des boissons (cleaning and sterilization chemicals)
In short, chemical flow meters are indispensable tools wherever chemical reactions, dilution, or dosage control depend on precise flow data.
The Importance and Challenges of Measuring Chemical Flow
Measuring chemical flow accurately is crucial not only for product quality and efficiencymais aussi pour safety and regulatory compliance. Many chemicals are corrosive, volatile, or toxic, and any mismeasurement can cause safety hazards, process inefficiencies, or environmental violations.
Why Chemical Flow Measurement Matters
- Accurate dosing and blending – Ensures correct chemical proportions in reactions and formulations.
- Process safety – Prevents leaks, overpressure, or dangerous reactions caused by incorrect chemical flow.
- Cost control – Reduces waste and optimizes resource consumption.
- Regulatory compliance – Maintains adherence to environmental and safety regulations.
Challenges in Chemical Flow Measurement
- Corrosive or reactive chemicals Many acids, alkalis, or solvents can corrode or degrade standard materials like stainless steel or aluminum. And the wetted part or even main part must use corrosion-resistant materials such as PTFE, PFA, PVDF, or Hastelloy.
- Varied viscosity and density Chemical fluids can range from low-viscosity solvents à highly viscous resins or oils. Some flow meters are sensitive to viscosity changes, making them unsuitable for certain applications.
- Temperature and pressure extremes Processes like polymerization or distillation can involve high temperatures (up to 300°C) et high pressures, which affect sensor accuracy and material compatibility.
- Presence of particulates or gas bubbles Slurries or aerated liquids can interfere with flow readings in volumetric or velocity-based flow meters.
- Hazardous environments Chemical plants often require explosion-proof or intrinsically safe flow meters certified for use in hazardous areas (ATEX, IECEx).
For these reasons, selecting a proper chemical flow meter requires careful consideration of both the chemical properties et operating conditions.
Recommended Flow Meter Types for Chemical Applications
Not all flow meters are suitable for chemicals. Below are the most common types recommended for measuring different kinds of chemical fluids, along with their working principles, advantages, and limitations.
Débitmètres massiques à effet Coriolis
Principe de fonctionnement :
Coriolis flow meters measure the débit massique of fluids by detecting the deflection caused by fluid movement through vibrating tubes.
Principaux avantages :
- Direct measurement of débit massique (no need for density compensation)
- High accuracy (±0.1–0.2%)
- Convient pour liquids, slurries, and gases
- Fonctionne bien pour high-viscosity or corrosive chemicals
Limites :
- Coût initial plus élevé
- Sensitive to vibration
Meilleur pour :
High-value or critical processes such as acid dosing, solvent delivery, polymer productionet pharmaceutical manufacturing.
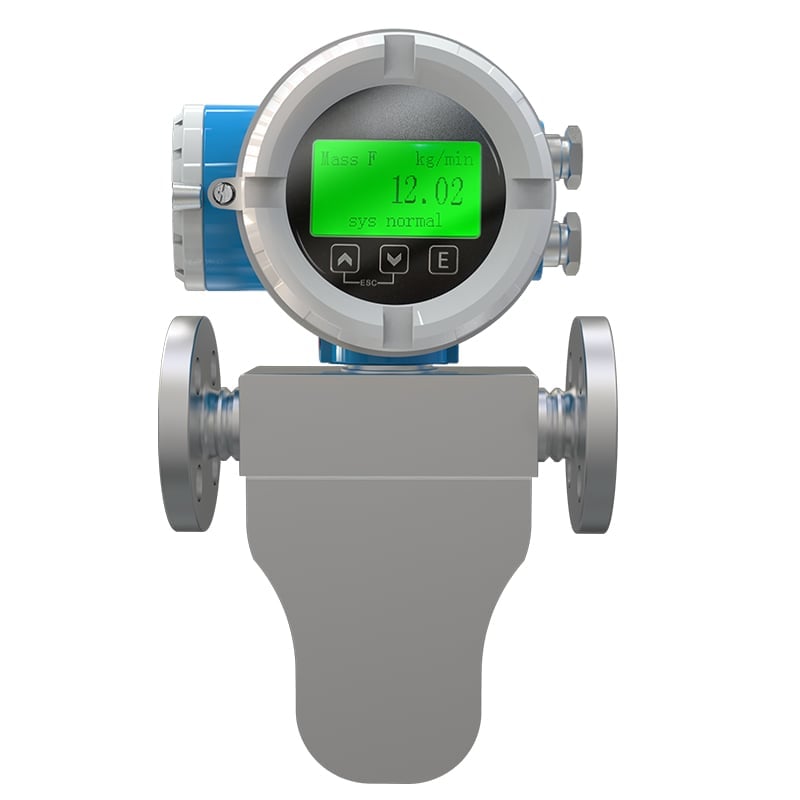

- Haute précision jusqu'à ±0,1 %, Bonne fiabilité
- Bonnes performances en matière de stabilité zéro et d'anti-interférence
- Pas de pièces mobiles, pas d'entretien nécessaire
- Communication numérique multiple, y compris Hart
Débitmètres massiques thermiques
Principe de fonctionnement :
These meters measure gas flow by detecting the heat dissipation caused by the gas moving past a heated sensor element.
Principaux avantages :
- Idéal pour chemical gases like nitrogen, hydrogen, or chlorine
- Direct mass flow measurement (independent of pressure and temperature)
- No moving parts — low maintenance
Limites :
- Limited to des gaz propres et secs. Here’re more ideas for débitmètres de gaz.
- Not suitable for liquids or wet gas mixtures
Meilleur pour :
Monitoring chemical gas flow in inerting systems, gas blending, or leak detection.
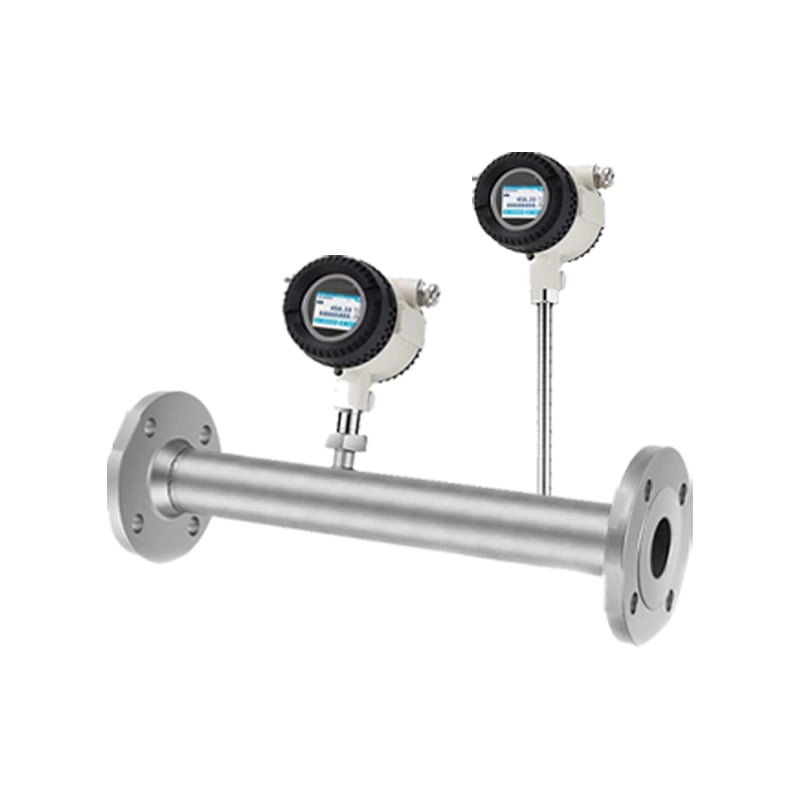

Débitmètres massiques thermiques
- Classe antidéflagrante : Ex db IIC T6 Gb / Ex tb IIIC T80°CDb.
- Médium : Air comprimé, azote, oxygène, dioxyde de carbone et autres gaz sans condensation.
- Rapport de réduction ultra large de 1:2500, la plage de mesure s'étend de 0,1 Nm/s à 250 Nm/s.
- Traitement entièrement numérique du signal, plus grande précision, stabilité à long terme.
Débitmètres magnétiques
Principe de fonctionnement :
Débitmètres magnétiques operate based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, measuring voltage generated by conductive fluids passing through a magnetic field.
Principaux avantages :
- Pas de pièces mobiles
- Excellent for corrosive, conductive liquids
- High accuracy even with varying viscosity
Limites :
- Only suitable for liquides conducteurs
Meilleur pour :
Acids, bases, salt solutions, wastewateret chemical slurries.
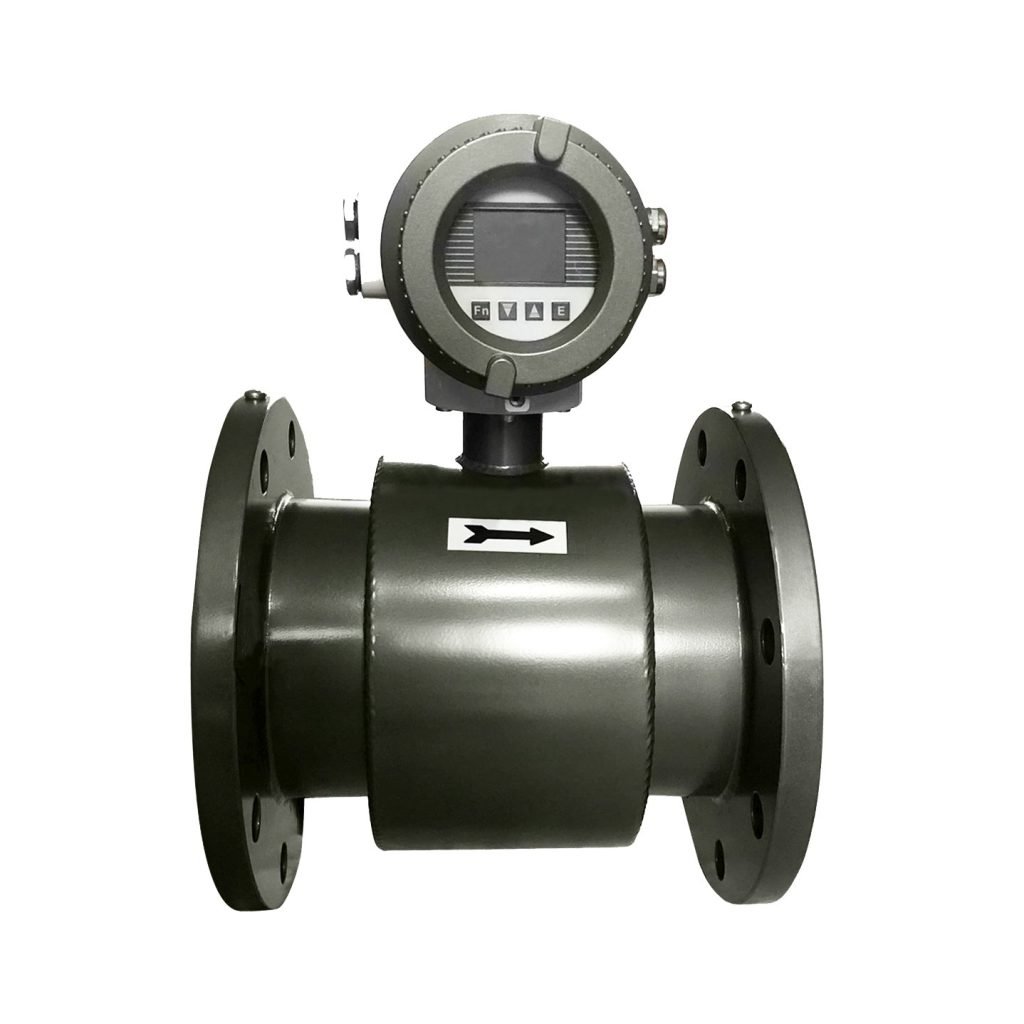

Débitmètres électromagnétiques
- Revêtement en PU, PFA, ETFE ou FEP : excellente résistance aux produits chimiques et à l'abrasion.
- Wide range of electrode materials, including corrosion-resistant materials like Hastelloy.
- High accuracy up to ±0.2 %
Débitmètres à déplacement positif
Principe de fonctionnement :
These meters physically trap a fixed volume of fluid and count how many times the chamber fills and empties.
Principaux avantages :
- Excellent for fluides à haute viscosité like oils, adhesives, or resins. Most recommended for débitmètres d'huile et débitmètres de carburant.
- High accuracy even at low flow rates
- Independent of flow profile and pipe orientation
Limites :
- Contains moving parts that require maintenance
- Not suitable for abrasive or particulate-laden fluids
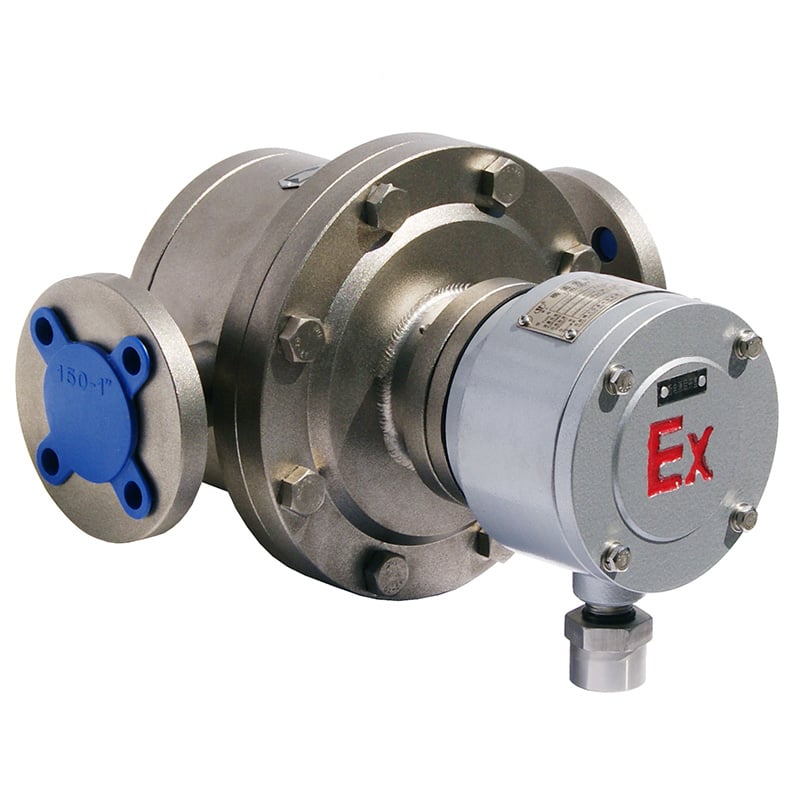

Débitmètres à déplacement positif
- Fonctionnement régulier du rotor en spirale avec un minimum de vibrations pour des performances constantes
- Large plage de mesure avec une bonne répétabilité
- Mesures de haute précision jusqu'à ±0,2%
- Insensible au changement de viscosité
- Optimisé pour la mesure des liquides à haute viscosité
Meilleur pour :
Lubricants, paints, polymerset non-corrosive chemical liquids.
Débitmètres à ultrasons
Principe de fonctionnement :
Ultrasonic flow meters measure flow rate using sound waves — either by the temps de transit ou Doppler method.
Principaux avantages :
- Non intrusif (clamp-on type available)
- Works for both conductive and non-conductive fluids
- Convient pour corrosive or sterile processes
Limites :
- Accuracy affected by bubbles or suspended solids
- Requires a clean pipe surface for clamp-on installation
Meilleur pour :
Solvents, cooling liquids, and corrosive acids where contamination must be avoided.
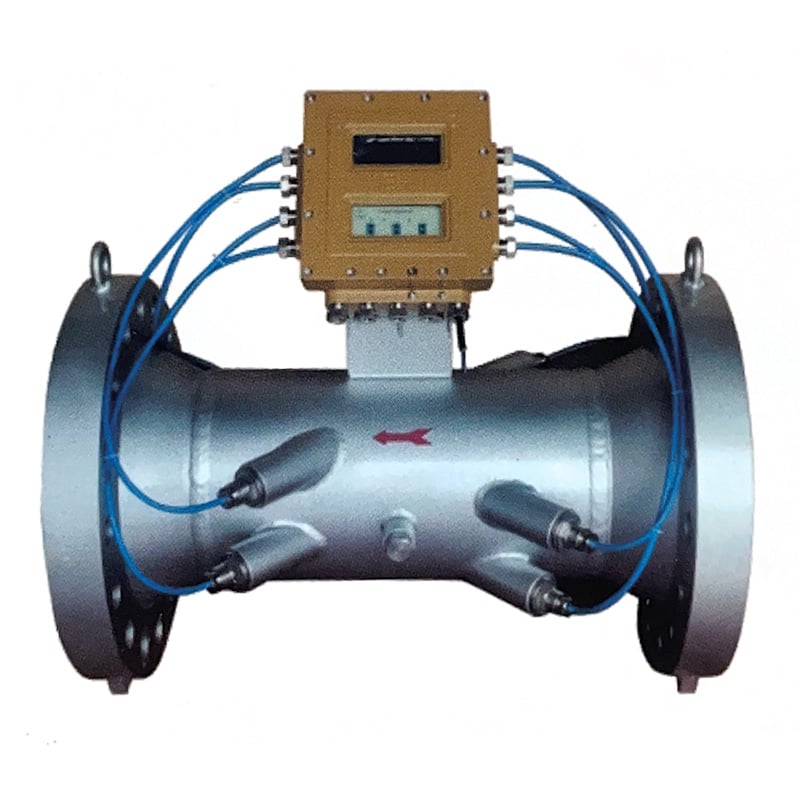

- Haute précision pour les gaz jusqu'à ±0,5%
- Pas de pièces mobiles, pas de perte de pression, pas d'obstruction de la ligne
- Pas de lubrification ni d'entretien périodique
- La mesure n'est pas affectée par les propriétés du gaz
- Rapport de réduction large de 100:1
- Capacité bidirectionnelle
Gas Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs)
Principe de fonctionnement :
MFCs combine a mass flow sensor, a valve, and a control circuit to precisely measure and control gas flow in real-time.
Principaux avantages :
- Provides precise flow control, not just measurement
- Compact and suitable for laboratory or pilot-scale processes
- Fonctionne bien avec reactive or specialty gases
Limites :
- Designed primarily for faibles débits
Meilleur pour :
Gas mixing, coating processes, and catalyst research.
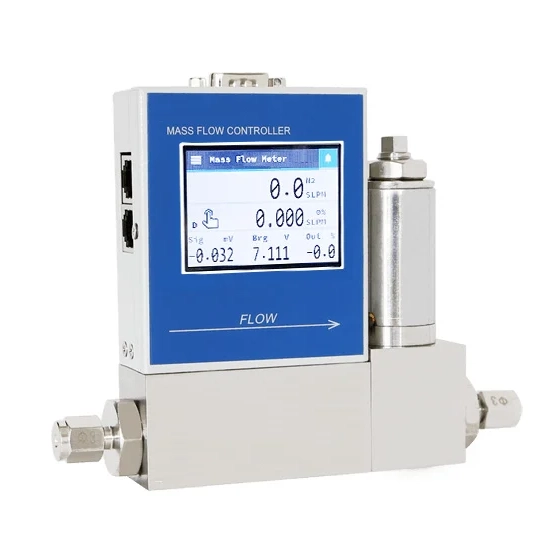

- Designed for low flow gas / liquid measuring
- It can measure high viscosity fluid and high density gas
- Designed for low flow gas / liquid measuring
- Contrôleur PID intégré pour réguler le débit
- Mesure directe du débit massique, compensation automatique de la température
How to Choose the Right Chemical Flow Meter
Selecting the correct chemical flow meter requires evaluating several technical and chemical parameters. Below are the main criteria to guide your selection:
1. Identify the Chemical Properties
- Corrosivité: Choose materials like PTFE, PFA, or Hastelloy for aggressive acids or alkalis.
- Conductivité: Use débitmètres magnétiques for conductive fluids; for non-conductive fluids, consider ultrasonic or Coriolis types.
- Viscosité: For viscous fluids, déplacement positif ou Coriolis flow meters perform better.
2. Define the Flow Range and Pipe Size
Each meter has an optimal flow range. Oversized or undersized meters will reduce accuracy. Always match the flow meter’s range to your process flow rate.
3. Operating Conditions
- Temperature and pressure must be within the meter’s limits.
- In hazardous environments, select explosion-proof ou intrinsically safe models.
4. Installation Requirements
- Consider available space, orientation, and maintenance access.
- Some flow meters (like ultrasonic clamp-on types) are ideal when pipe modification is not possible.
5. Output and Communication
Modern chemical flow meters support 4–20 mA, Modbus, HART, or digital outputs for integration into process control systems.
6. Accuracy and Maintenance
If precision is critical (e.g., chemical blending or dosing), choose Coriolis ou débitmètres magnétiques. Some suppliers also provide very high accuracy PD flow meters like Metlan Instruments.
A chemical flow meter plays a vital role in controlling and monitoring chemical processes with accuracy and safety. Because of the diversity of chemical fluids — from corrosive acids to viscous oils — there is no single flow meter suitable for all situations. Ultimately, the right flow meter should match the chemical’s physical properties, the process conditions, and the required accuracy.
About Metlan Instruments Chemical Flow Meters
Au Metlan Instruments, we specialize in high-precision flow measurement and control solutions for industrial applications. Our product range includes débitmètres massiques thermiques, Débitmètres massiques à effet Coriolis, positive displacement meterset mass flow controllers designed for both gases and liquids — including corrosive and specialty chemicals.
With advanced sensor technology and robust materials, Metlan Instruments ensures long-term stability, corrosion resistance, and exceptional accuracy — helping chemical plants, laboratories, and process industries achieve precise and reliable flow measurement.